An EPIC View Of Earth
An EPIC View of Earth
“Look again at that dot. That’s here. That’s home. That’s us.”
Carl Sagan wrote those words in his book Pale Blue Dot: A Vision For The Human Future In Space. His now-famous ode to our home planet (listen to the full passage here, in animated form) is perhaps our most poignant and humble reminder of the exquisite beauty and shared fragility of this planet we call home.
NASA is now bringing us a daily reminder of that message, thanks to the EPIC camera (a very appropriately named camera, in my opinion) on board NOAA’s DSCOVR satellite. You can see some of its handiwork in the image sequence above.
DSCOVR’s official space job is to observe weather on and around the sun, to extend its mechanical finger into the solar wind and measure how strongly that stream of charged particles is gusting toward Earth. It does this job from a special spot in space called the L1 Lagrange point. If you were to draw a line between us and the sun, DSCOVR would be sitting along it, like so (not to scale):

That’s a convenient place to put a spacecraft, especially one whose job it is to stare at the sun. See, DSCOVR is nestled inside a pocket where it’s tugged equally by the Earth’s and Sun’s gravity, like a stalemate in an orbital game of tug-o-war. Gravity does all the work, and the spacecraft doesn’t need to maneuver much to stay in position. There’s a few of these gravity-neutral Lagrange points out there, as you can tell in the image above, and we’ve got spacecraft residing at all of them.
As a side effect of its sun-staring mission, DSCOVR’s backside happens to be looking back at Earth full-time. In a way, I think that makes it a different sort of moon.
NASA doesn’t like to let any opportunity go un-scienced, of course, so they decided to slap a camera on DSCOVR’s rear, the one named EPIC, and use their stable perch to keep a regular eye on us. Good lookin’ out, NASA.
A little change in perspective can do a planet good. In 1990, from a vantage point beyond Pluto, Voyager 1 turned its cameras back toward home to take one last look, giving us the image that inspired Carl Sagan’s ode to ol’ Dotty Blue:

This was not an easy shot to take. Voyager’s camera wasn’t the fancy digital type like most of us have in our phones. It was essentially an old-fashioned black and white tube TV in reverse, relying on colored filters held in front of the camera to highlight different wavelengths of light. Voyager stored its image data on magnetic tape, and each of the shots took more than five hours to reach Earth. Sagan and NASA’s planetary science team had to practically move the heavens (since they were unable to move the Earth) in order to take that picture.
Now consider the effect this picture has had. That’s home. That’s us. Even if you weren’t born in 1990, everyone and everything that made you is in and on that hazy blue speck. I hope you never lose sight of how amazing it is to view our planet from this perspective.
Luckily, you can get a reminder every day. The DSCOVR satellite is now sending roughly a picture an hour back to Earth, 24/7/365. That’s a near real-time view of our home. Go take a look. It’s pretty epic.
To see a daily look at what a day on Earth looks like, check out EPIC’s daily updates here.
More Posts from Dotmpotter and Others











Breathtaking Images of Underwater Life Captured by Freediving Photographers Alex Voyer and Alex Roubaud


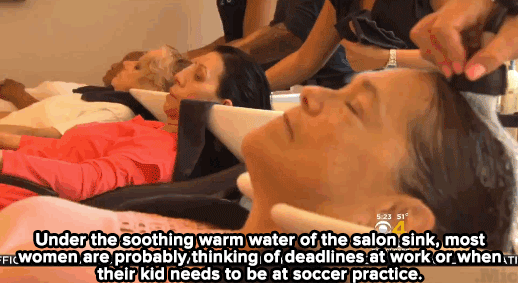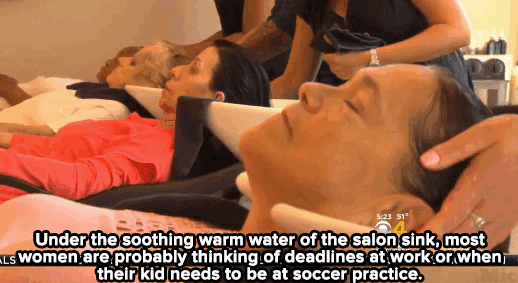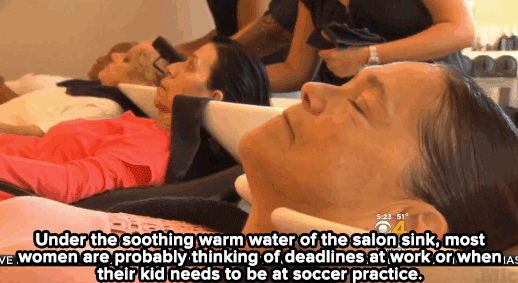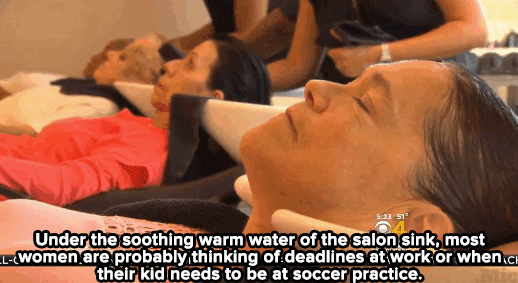
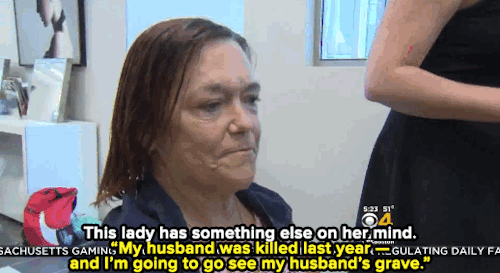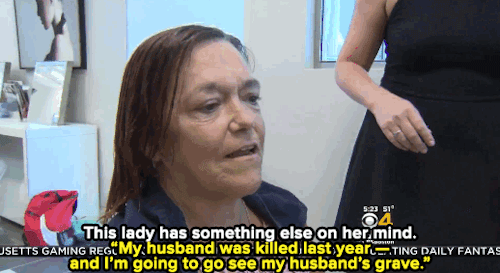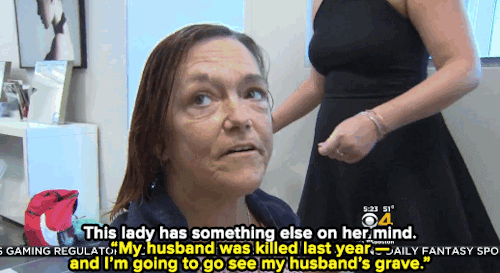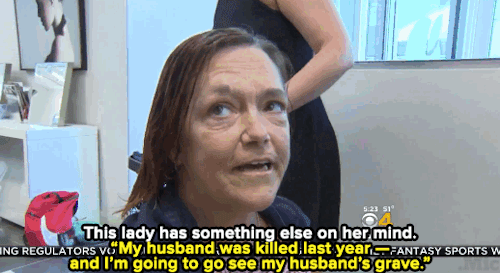






Watch: A haircut may not solve homelessness — but it can make all the difference for these women.
Follow @stylemic





For more on the Fermi Paradox and why alien life hasn’t found us yet. (Infographic via futurism)
It is easy to see where we are heading – the future will need far fewer workers. Computers, automation and robots will eliminate jobs in increasingly large numbers, and also apply downward wage pressure. Which is completely backwards from what could be happening if we designed society for the benefit of all. If the wealth were not concentrating, every worker would be benefiting from the increases in productivity created by all of this new technology. Wages would be rising and the work week would be shortening. Instead, all of the benefits are flowing straight to the 1% and everyone else is suffering.
This is where the idea of the Basic Income comes in. It is a standardized way of addressing the large scale unemployment that is coming soon, as well as simplifying welfare, retirement and disability payments, as well as making the productivity increases available to everyone in society instead of the elite few.
The idea is simple: everyone in society receives a regular income simply for being alive. The ultimate goal is for the Basic Income payment, by itself, to provide a comfortable living for every member of society without working.
Byzantine 'flat-pack' church to be reconstructed in Oxford after spending 1,000 years on the seabed

Centuries before the Swedes started flat-packing their furniture, the Holy Roman Emperor Justinian had his own version, sending self-assembly churches to newly conquered parts of his empire.
Now one of the “Ikea-style” churches, which spent more than 1,000 years on a seabed after the ship carrying it sank, is to be reconstructed for the first time in Oxford.
The Byzantine church will be on display at the Ashmolean Museum of Art and Archaeology as part of the exhibition Storms, War and Shipwrecks: Treasures from the Sicilian Seas, opening in June.
Paul Roberts, co-curator of the exhibition, said: “Everything in the exhibition will be from under the sea. It’s very different from what’s been done before. Read more.

Artificial optical materials could allow cheaper, flatter, more efficient detectors for night vision and other uses
A new way of taking images in the mid-infrared part of the spectrum, developed by researchers at MIT and elsewhere, could enable a wide variety of applications, including thermal imaging, biomedical sensing, and free-space communication.
The mid-infrared (mid-IR) band of electromagnetic radiation is a particularly useful part of the spectrum; it can provide imaging in the dark, trace heat signatures, and provide sensitive detection of many biomolecular and chemical signals. But optical systems for this band of frequencies have been hard to make, and devices using them are highly specialized and expensive. Now, the researchers say they have found a highly efficient and mass-manufacturable approach to controlling and detecting these waves.
The findings are reported in the journal Nature Communications, in a paper by MIT researchers Tian Gu and Juejun Hu, University of Massachusetts at Lowell researcher Hualiang Zhang, and 13 others at MIT, the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, and the East China Normal University.
The new approach uses a flat, artificial material composed of nanostructured optical elements, instead of the usual thick, curved-glass lenses used in conventional optics. These elements provide on-demand electromagnetic responses and are made using techniques similar to those used for computer chips. “This kind of metasurface can be made using standard microfabrication techniques,” Gu says. “The manufacturing is scalable.”
Read more.

The UK’s first new nuclear power station for a generation will cost electricity customers at least £4.4bn and the subsidy bill could reach £20bn, the government has revealed.
The charges, which will be passed on to nearly 30 million customers, are a result of ministers’ decision to guarantee the new Hinkley Point C operators £92.50 for every unit of electricity – more than double the current market price.
It comes less than a week after the government admitted the £24bn plant in Somerset will be subsidised – something it denied throughout the last parliament.
Details of the costs – an average of about £150 to £660 per customer over the 35 years of the deal – are exposed in a document quietly put before parliament last week and which has only just come to light.
(via Hinkley Point C will cost customers at least £4.4bn | Environment | The Guardian)

A Merry-Go-Round That Turns The Power Of Play Into Electricity - Vlad Vilenski posted in Green, Electricity and Non Profit
Empower Playgrounds is a nonprofit that has come up with an intriguing solution: Harnessing the power of play, it provides merry-go-rounds to schools in Ghana that generate and store electricity as they are spun around, even while teeming with laughing and smiling kids.
Continue to fastcodesign.com

Ever wonder how coal formed?
-
 deadlysunlight liked this · 2 years ago
deadlysunlight liked this · 2 years ago -
 it-build-restore reblogged this · 5 years ago
it-build-restore reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 stanfave reblogged this · 5 years ago
stanfave reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ssolson liked this · 5 years ago
ssolson liked this · 5 years ago -
 madprohetess reblogged this · 5 years ago
madprohetess reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 madprohetess liked this · 5 years ago
madprohetess liked this · 5 years ago -
 peacefulrestvalley liked this · 6 years ago
peacefulrestvalley liked this · 6 years ago -
 youlookverywowtonight liked this · 6 years ago
youlookverywowtonight liked this · 6 years ago -
 simplygreenie liked this · 6 years ago
simplygreenie liked this · 6 years ago -
 hottreesinurarea liked this · 6 years ago
hottreesinurarea liked this · 6 years ago -
 tehyablue-blog liked this · 6 years ago
tehyablue-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 everybodygotawaterbuffalo liked this · 6 years ago
everybodygotawaterbuffalo liked this · 6 years ago -
 notworththeeffort2 liked this · 6 years ago
notworththeeffort2 liked this · 6 years ago -
 cuteloonyinlove reblogged this · 6 years ago
cuteloonyinlove reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 cuteloonyinlove liked this · 6 years ago
cuteloonyinlove liked this · 6 years ago -
 vennitrii liked this · 6 years ago
vennitrii liked this · 6 years ago -
 wachsurfer2018 liked this · 6 years ago
wachsurfer2018 liked this · 6 years ago -
 gobletofrock reblogged this · 8 years ago
gobletofrock reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 covenantofcats liked this · 8 years ago
covenantofcats liked this · 8 years ago -
 iamsimbad liked this · 8 years ago
iamsimbad liked this · 8 years ago -
 oppsforeverhi-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
oppsforeverhi-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 oppsforeverhi-blog liked this · 8 years ago
oppsforeverhi-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 letters-from-the-sky1 reblogged this · 8 years ago
letters-from-the-sky1 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 letters-from-the-sky1 liked this · 8 years ago
letters-from-the-sky1 liked this · 8 years ago -
 absurdistocchiolism reblogged this · 8 years ago
absurdistocchiolism reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 absurdistocchiolism liked this · 8 years ago
absurdistocchiolism liked this · 8 years ago -
 imnotthepancakelady liked this · 8 years ago
imnotthepancakelady liked this · 8 years ago -
 infinite--cosmos-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
infinite--cosmos-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 infinite--cosmos-blog liked this · 8 years ago
infinite--cosmos-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 sketchylime liked this · 8 years ago
sketchylime liked this · 8 years ago -
 idek-idec-idegaf liked this · 8 years ago
idek-idec-idegaf liked this · 8 years ago -
 imadethisblogbecauseofmegacon reblogged this · 8 years ago
imadethisblogbecauseofmegacon reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 nx-ked liked this · 8 years ago
nx-ked liked this · 8 years ago -
 celestialcum liked this · 8 years ago
celestialcum liked this · 8 years ago -
 deliriousmonkeythomas-blog liked this · 8 years ago
deliriousmonkeythomas-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 ncarrion reblogged this · 8 years ago
ncarrion reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ncarrion liked this · 8 years ago
ncarrion liked this · 8 years ago -
 a-d-v-e-n-t-u-r-e-s liked this · 8 years ago
a-d-v-e-n-t-u-r-e-s liked this · 8 years ago -
 the-gangs-all-queer liked this · 9 years ago
the-gangs-all-queer liked this · 9 years ago