Cylinder Fragments - 230322

Cylinder Fragments - 230322
More Posts from Epic-flight and Others

Clouds, swimming in fractals 2021
new animated work!

The Dark Seahorse in Cepheus : Light-years across, this suggestive shape known as the Seahorse Nebula appears in silhouette against a rich, luminous background of stars. Seen toward the royal northern constellation of Cepheus, the dusty, obscuring clouds are part of a Milky Way molecular cloud some 1,200 light-years distant. It is also listed as Barnard 150 (B150), one of 182 dark markings of the sky cataloged in the early 20th century by astronomer E. E. Barnard. Packs of low mass stars are forming within, but their collapsing cores are only visible at long infrared wavelengths. Still, the colorful stars of Cepheus add to this pretty, galactic skyscape. via NASA
🤠🤠🤠🤠


(Link)

Icosa Glass - 210406
Boo-tiful Ring Galaxies

A ghoulish secret lurks within each of these gorgeous galaxies. Their rings are dotted with stellar graveyards!

These objects are called ring galaxies, and scientists think most of them form in monster-sized crashes. Not just any galaxy collision will do the trick, though. To produce the treat of a ring, a smaller galaxy needs to ram through the center of a larger galaxy at just the perfect angle.

The collision causes ripples that disturb both galaxies. The gravitational shock causes dust, gas, and stars in the larger galaxy’s disk to rush outward. As this ring of material plows out from the galaxy’s center, gas clouds collide and trigger the birth of new stars.

In visible light, the blue areas in the galaxies’ rings show us where young, hot stars are growing up. Faint, pink regions around the ring mark stellar nurseries where even younger stars set hydrogen gas aglow.
The newborn stars come in a mix of sizes, from smaller ones like our Sun all the way up to huge stars with tens of times the Sun’s mass. And those massive stars live large!
While a star like our Sun will last many billions of years before running out of fuel, larger stars burn much brighter and faster. After just a few million years, the largest stars explode as supernovae. When massive stars die, they leave behind a stellar corpse, either a neutron star or black hole.

When we turn our X-ray telescopes to these ring galaxies, we see telltale signs of stellar remnants dotted throughout their ghostly circles. The purple dots in the X-ray image above are neutron stars or black holes that are siphoning off gas from a companion star, like a vampire. The gas reinvigorates stellar corpses, which heat up and emit X-rays. These gas-thirsty remains are beacons lighting the way to stellar graveyards.
Spiral galaxies — like our home galaxy, the Milky Way — have curved arms that appear to sweep out around a bright center. The dust and gas in those spiral arms press together, causing cycles of star formation that result in a more even mix of new stars and stellar corpses scattered throughout our galaxy. No creepy ring of stellar corpses here!
To visit some other eerie places in the universe, check out the latest additions to the Galaxy of Horrors poster series and follow NASA Universe on Twitter and Facebook for news about black holes, neutron stars, galaxies, and all the amazing objects outside our solar system.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
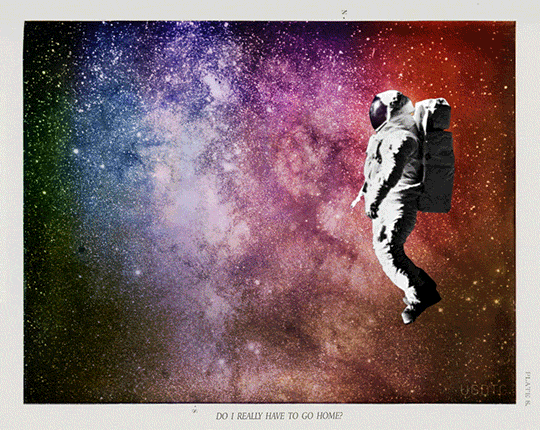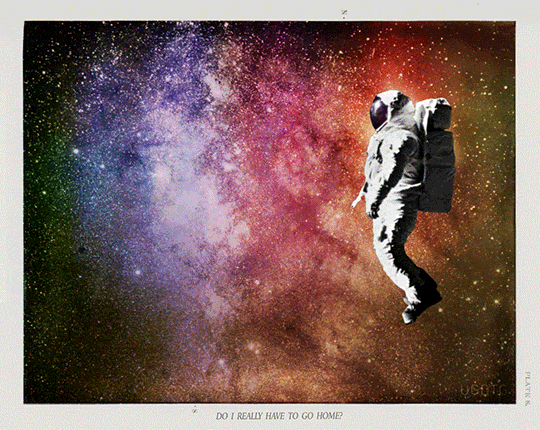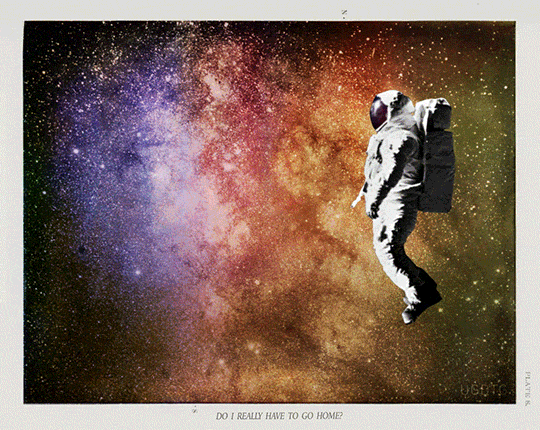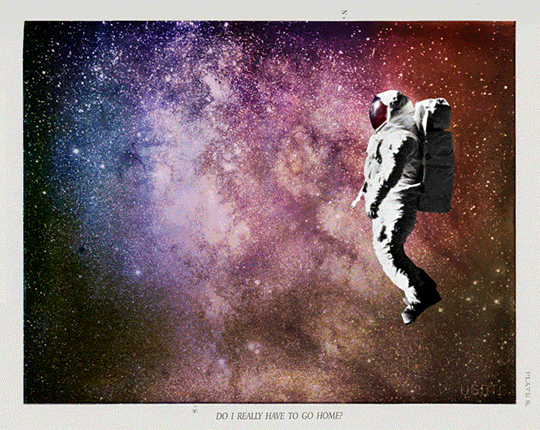
Proposal for GIF IT UP 2016

Scorpius Rising, photographed from Mt. Laguna, California. (Hendren Imaging)

Pulling Away.
You can get this GIF as a phone wallpaper for free through the Zedge app.
You can also get this GIF as a looping 1080p video if you support me on Patreon.
Twitter / Instagram / Shop / Gumroad / Patreon / Zedge

Starbright.
Twitter / Instagram / Gumroad / Patreon
KnownOrigin / SuperRare / OBJKT /Zedge
-
 epic-flight reblogged this · 1 year ago
epic-flight reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 galvesgal liked this · 1 year ago
galvesgal liked this · 1 year ago -
 snowqueen-gh liked this · 2 years ago
snowqueen-gh liked this · 2 years ago -
 fragrance-34 reblogged this · 2 years ago
fragrance-34 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 fragrance-34 liked this · 2 years ago
fragrance-34 liked this · 2 years ago -
 nothingamazing liked this · 2 years ago
nothingamazing liked this · 2 years ago -
 vladstrain liked this · 2 years ago
vladstrain liked this · 2 years ago -
 hercuels liked this · 2 years ago
hercuels liked this · 2 years ago -
 unlikelypatrolgiantmonger-blog liked this · 2 years ago
unlikelypatrolgiantmonger-blog liked this · 2 years ago -
 axeltornadoes liked this · 2 years ago
axeltornadoes liked this · 2 years ago -
 ericaofreblogs reblogged this · 2 years ago
ericaofreblogs reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 lobo214 liked this · 2 years ago
lobo214 liked this · 2 years ago -
 nwashy reblogged this · 2 years ago
nwashy reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 foilflingza liked this · 2 years ago
foilflingza liked this · 2 years ago -
 rsrsbabe420 reblogged this · 2 years ago
rsrsbabe420 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 rsrsbabe420 liked this · 2 years ago
rsrsbabe420 liked this · 2 years ago -
 politoke reblogged this · 2 years ago
politoke reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 arthemysia liked this · 2 years ago
arthemysia liked this · 2 years ago -
 stonerparty reblogged this · 2 years ago
stonerparty reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 fragrance-34 reblogged this · 2 years ago
fragrance-34 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 lunaraen reblogged this · 2 years ago
lunaraen reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 eldeljazz64 liked this · 2 years ago
eldeljazz64 liked this · 2 years ago -
 bufffalo liked this · 2 years ago
bufffalo liked this · 2 years ago -
 lunaraen liked this · 2 years ago
lunaraen liked this · 2 years ago -
 ghostlylights reblogged this · 2 years ago
ghostlylights reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 dnotive reblogged this · 2 years ago
dnotive reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 territorialinstinct reblogged this · 2 years ago
territorialinstinct reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 vanged-lunterra liked this · 2 years ago
vanged-lunterra liked this · 2 years ago -
 m00ndingochan reblogged this · 2 years ago
m00ndingochan reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 444maseaux liked this · 2 years ago
444maseaux liked this · 2 years ago -
 m00ndingochan liked this · 2 years ago
m00ndingochan liked this · 2 years ago -
 itsnicolecage liked this · 2 years ago
itsnicolecage liked this · 2 years ago -
 catlover333sworld reblogged this · 2 years ago
catlover333sworld reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 catlover333sworld liked this · 2 years ago
catlover333sworld liked this · 2 years ago -
 lilyannlove liked this · 2 years ago
lilyannlove liked this · 2 years ago -
 impivm liked this · 2 years ago
impivm liked this · 2 years ago -
 black-storm-dark reblogged this · 2 years ago
black-storm-dark reblogged this · 2 years ago

