Intergalacticnerd - Space N Shit
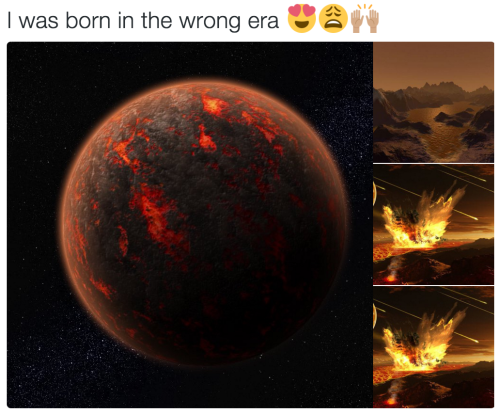

More Posts from Intergalacticnerd and Others

Comet PanSTARRS and the Helix Nebula : Its rare that such different objects are imaged so close together. Such an occasion is occurring now, though, and was captured two days ago in combined parallel exposures from the Canary Islands of Spain. On the lower right, surrounded by a green coma and emanating an unusually split blue ion tail diagonally across the frame, is Comet C/2013 X1 . This giant snowball has been falling toward our Sun and brightening since its discovery in 2013. Although Comet PannSTARRS is a picturesque target for long-duration exposures of astrophotography, it is expected to be only barely visible to the unaided eye when it reaches its peak brightness in the next month. On the upper left, surrounded by red-glowing gas, is the also-picturesque Helix Nebula. At 700 light years distant, the Helix is not only much further away than the comet, but is expected to retain its appearance for thousands of years. via NASA
js
deep sea documentaries have me like


The Belt of Venus is a pink glowing arch seen across the sky when the shadow of the Earth’s translucent atmosphere casts a shadow back upon itself.
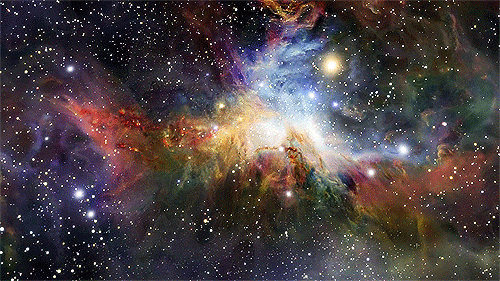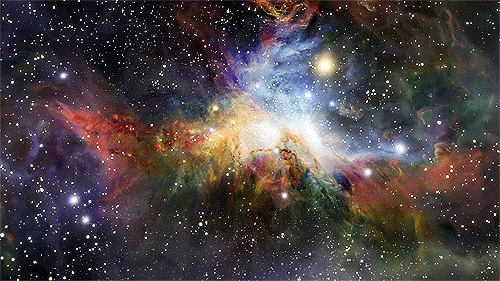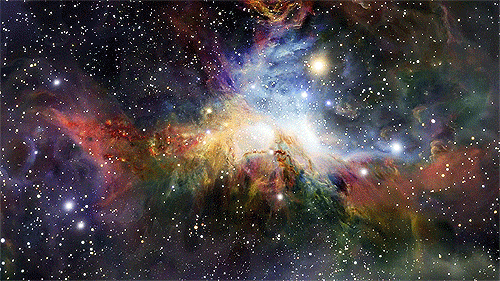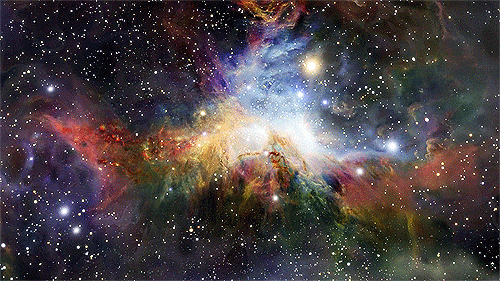



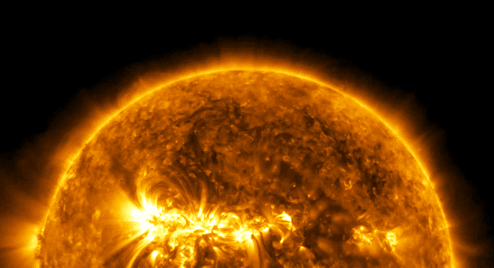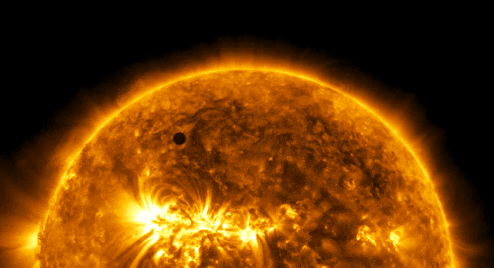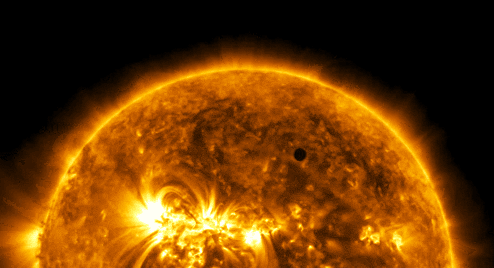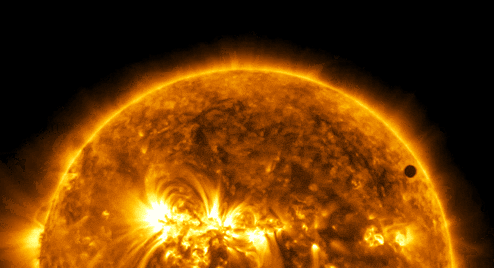
“Every one of us is, in the cosmic perspective, precious. If a human disagrees with you, let them live. In a hundred billion galaxies, you will not find another.” ~ Carl Sagan, Cosmos

Southern Cross by Carlos Fairbairn
js

Infant Star’s Artistic Outburst
The artistic outburst of an extremely young star, in the earliest phase of formation, is captured in this spectacular image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. The colourful wisps, found in the lower left of the image, are painted onto the sky by a young star cocooned in the partially illuminated cloud of obscuring dust seen to the upper right.
Pictured punching through the enshrouding dust is an extremely hot, blue jet of gas released by the young star. As this jet speeds through space, it collides with cooler surrounding material. The result is the colourful object to the lower left, produced as the cooler material is heated by the jet (opo9524a, potw1307a).
This wispy object is known as HH34 and it is an example of a Herbig–Haro (HH) object. It resides approximately 1400 light-years away near the Orion Nebula, a large star formation region within the Milky Way. HH objects exist for a cosmically brief time — typically thousands of years — with changes seen in observations taken only a few years apart (heic1113).
Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA







Valles Marineris: The Grand Canyon of Mars
Image Credit: Viking Project, USGS, NASA
The largest canyon in the Solar System cuts a wide swath across the face of Mars. Named Valles Marineris, the grand valley extends over 3,000 kilometers long, spans as much as 600 kilometers across, and delves as much as 8 kilometers deep. By comparison, the Earth’s Grand Canyon in Arizona, USA is 800 kilometers long, 30 kilometers across, and 1.8 kilometers deep. The origin of the Valles Marineris remains unknown, although a leading hypothesis holds that it started as a crack billions of years ago as the planet cooled. Several geologic processes have been identified in the canyon. The above mosaic was created from over 100 images of Mars taken by Viking Orbiters in the 1970s.

All Quiet in the Nursery?
The dark patch snaking across this spectacular image of a field of stars in the constellation of Ophiuchus (The Serpent-bearer) is not quite what it appears to be.
Although it looks as if there are no stars here, they are hidden behind this dense cloud of dust that blocks out their light. This particular dark cloud is known as LDN 1768.
Despite their rather dull appearance, dark nebulae like LDN 1768 are of huge interest to astronomers, as it is here that new stars form. Inside these vast stellar nurseries there are protostars — stars at the earliest stage of their lives, still coalescing out of the gas and dust in the cloud.
Eventually, the protostars will become dense and hot enough to start the nuclear reactions that will produce visible light and they will start to shine. When this happens, they will blow away the cocoon of dust surrounding them and cause any remaining gas to emit light as well, creating the spectacular light show known as an HII region.
Credit: ESO








Alexander Pohl
-
 luziesalt reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
luziesalt reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 luziesalt liked this · 3 weeks ago
luziesalt liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 many-many-bubbles reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
many-many-bubbles reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 endystar liked this · 3 weeks ago
endystar liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 arcanegemini reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
arcanegemini reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 ollier12 liked this · 3 weeks ago
ollier12 liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 shining-dawn reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
shining-dawn reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 ekolikeshorses liked this · 1 month ago
ekolikeshorses liked this · 1 month ago -
 too-hopeful-i-am liked this · 1 month ago
too-hopeful-i-am liked this · 1 month ago -
 enbylesbie reblogged this · 1 month ago
enbylesbie reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 kryptickurrency liked this · 1 month ago
kryptickurrency liked this · 1 month ago -
 hollowmations liked this · 1 month ago
hollowmations liked this · 1 month ago -
 badgerblitz reblogged this · 1 month ago
badgerblitz reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 badgerblitz liked this · 1 month ago
badgerblitz liked this · 1 month ago -
 catgirltoofies liked this · 1 month ago
catgirltoofies liked this · 1 month ago -
 ducttapebandages reblogged this · 1 month ago
ducttapebandages reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 hopper-jack reblogged this · 1 month ago
hopper-jack reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 ashkitty-love reblogged this · 1 month ago
ashkitty-love reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 0zwodder0 liked this · 1 month ago
0zwodder0 liked this · 1 month ago -
 sansationalpuns42 liked this · 1 month ago
sansationalpuns42 liked this · 1 month ago -
 chefenrir reblogged this · 1 month ago
chefenrir reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 chefenrir liked this · 1 month ago
chefenrir liked this · 1 month ago -
 sheepdude reblogged this · 1 month ago
sheepdude reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 hraeiou liked this · 1 month ago
hraeiou liked this · 1 month ago -
 lillypadcrochet liked this · 1 month ago
lillypadcrochet liked this · 1 month ago -
 willystamplerstits reblogged this · 1 month ago
willystamplerstits reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 coreytasticc reblogged this · 1 month ago
coreytasticc reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 juice-type-r reblogged this · 1 month ago
juice-type-r reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 juice-type-r liked this · 1 month ago
juice-type-r liked this · 1 month ago -
 tinycorvidae reblogged this · 1 month ago
tinycorvidae reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 kaiju420 reblogged this · 1 month ago
kaiju420 reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 kaiju420 liked this · 1 month ago
kaiju420 liked this · 1 month ago -
 mikaelness liked this · 1 month ago
mikaelness liked this · 1 month ago -
 blueberrythemoth liked this · 1 month ago
blueberrythemoth liked this · 1 month ago -
 blueberrythemoth reblogged this · 1 month ago
blueberrythemoth reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 mothmanbignaturals liked this · 1 month ago
mothmanbignaturals liked this · 1 month ago -
 negitivitron liked this · 1 month ago
negitivitron liked this · 1 month ago -
 alexstar reblogged this · 1 month ago
alexstar reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 ferncassette liked this · 1 month ago
ferncassette liked this · 1 month ago -
 this-cruel-kindness reblogged this · 1 month ago
this-cruel-kindness reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 enbylesbie liked this · 1 month ago
enbylesbie liked this · 1 month ago -
 evildurandoo liked this · 1 month ago
evildurandoo liked this · 1 month ago -
 arcanegemini liked this · 1 month ago
arcanegemini liked this · 1 month ago -
 vampire-squid-lesbian liked this · 1 month ago
vampire-squid-lesbian liked this · 1 month ago -
 nerdman2022 liked this · 1 month ago
nerdman2022 liked this · 1 month ago -
 bubblduck reblogged this · 1 month ago
bubblduck reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 bubblduck liked this · 1 month ago
bubblduck liked this · 1 month ago -
 milkteaspring liked this · 1 month ago
milkteaspring liked this · 1 month ago -
 wyldwayfarer liked this · 1 month ago
wyldwayfarer liked this · 1 month ago
"Astronomy compels the soul to look upwards and leads us from this world to another." - Plato
147 posts