Ritasakano - Outubros

More Posts from Ritasakano and Others
Solar System: 5 Things to Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, so let us break it down for you. Here are 5 things to know this week:
1. It’s Lunacy, Whether by Day or Night

What’s Up in the night sky during November? See all the phases of the moon by day and by night, and learn how to look for the Apollo landing sites. Just after sunset on November 13 and 14, look near the setting sun in the western sky to see the moon as a slender crescent. For more, catch the latest edition of the monthly “What’s Up” Tumblr breakdown.
2. Answer to Longstanding Mars Mystery is Blowin’ in the Wind

What transformed Mars from a warm and wet environment, one that might have supported surface life, to the cold, arid planet it is today? Data from our Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission pins much of the blame on the sun. Streams of charged solar particles crash against the Martian atmosphere, and without much of a magnetic field there to deflect the onslaught, over time the solar wind has stripped the air away.
3. Orbital Maneuvers in the Dark

The New Horizons mission team has set a new record. They recently performed the last in a series of trajectory changes that set the spacecraft on a course for an encounter with a Kuiper Belt object in January 2019. The Kuiper Belt consists of small bodies that orbit the sun a billion miles or more beyond Pluto. These latest course maneuvers were the most distant trajectory corrections ever performed by any spacecraft.
4. Visit Venus (But Not Really — You’d Fry)

Mars isn’t the only available destination. You can visit all the planets, moons and small worlds of the solar system anytime, right from your computer or handheld device. Just peruse our planets page, where you’ll find everything from basic facts about each body to the latest pictures and discoveries. Visit Venus HERE.
5. Titan Then and Now

Nov. 12 marks the 35th anniversary of Voyager 1’s Saturn flyby in 1980. Voyager saw Saturn’s enshrouded, planet-sized moon Titan as a featureless ball. In recent years, the Cassini mission haas revealed Titan in detail as a complex world. The spacecraft has peered beneath its clouds, and even delivered a probe to its encounter, which will include infrared scans, as well as using visible light cameras to look for methane clouds in the atmosphere.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
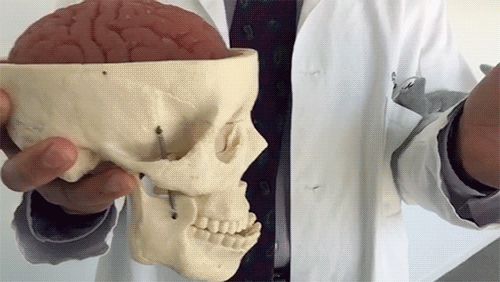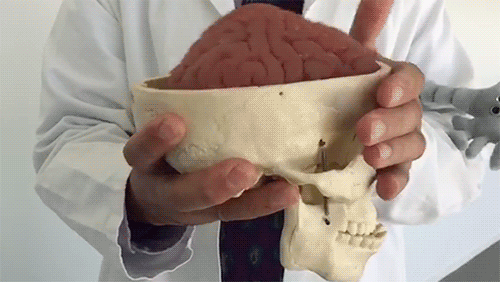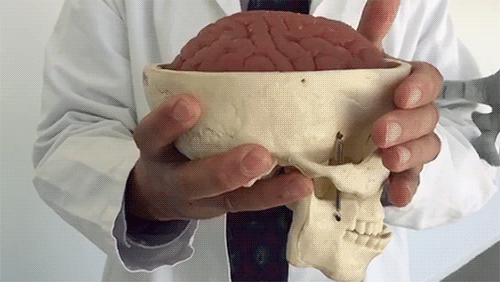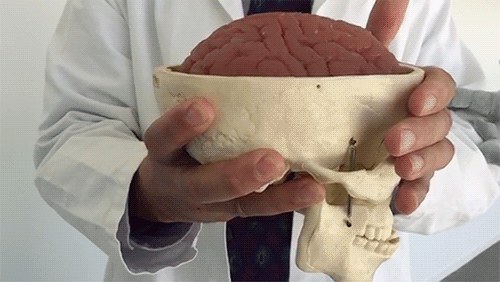
This is your brain experiencing a concussion
It may look like this model brain is made of Jell-O, but it’s the same consistency as a real brain.
As Dr. Christopher Giza from UCLA demonstrates, the brain is made of soft tissue and floats in fluid inside of the skull. When the skull moves quickly, the brain can jostle around a lot, which can lead to neurological symptoms.
“Most concussions are recoverable,” Giza said.
But concussions can be difficult to identify and some people suffer more serious symptoms, particularly after multiple concussions.
Lab studies have shown a “window of vulnerability” after a first concussion, Giza said. Concussed athletes are three to six times more likely to get another concussion. If they rush back to play, their reflexes, reaction time and thinking may be slower, putting them at risk of a second concussion and longer recovery period.
Six things parents and athletes need to know about concussions.
Empodere as mulheres!!



Fire Sprinklers Erupt from Ingeniously Camouflaged Huts to Protect a Historic Japanese Village

Noren - Tedomari Tsubame Niigata ken
Muitas vezes as imagens nos leva a mundos internos.

by Hisanori Manabe

Ao olhar Tudo parece simples Pontos Linhas Fios Juntos São a obra A criação A arte Simples tudo parece.
Ransomware
Entenda o que é ransomware: o malware que sequestra computadores http://www.tecmundo.com.br/seguranca-de-dados/116360-especialista-explica-crescimento-ransomware-brasil.htm
Incrível a projeção da explosão e a Terra. Vivas a distância!!!
The Sun Just Released the Most Powerful Flare of this Solar Cycle
The Sun released two significant solar flares on Sept. 6, including one that clocked in as the most powerful flare of the current solar cycle.
The solar cycle is the approximately 11-year-cycle during which the Sun’s activity waxes and wanes. The current solar cycle began in December 2008 and is now decreasing in intensity and heading toward solar minimum, expected in 2019-2020. Solar minimum is a phase when solar eruptions are increasingly rare, but history has shown that they can nonetheless be intense.

Footage of the Sept. 6 X2.2 and X9.3 solar flares captured by the Solar Dynamics Observatory in extreme ultraviolet light (131 angstrom wavelength)
Our Solar Dynamics Observatory satellite, which watches the Sun constantly, captured images of both X-class flares on Sept. 6.
Solar flares are classified according to their strength. X-class denotes the most intense flares, followed by M-class, while the smallest flares are labeled as A-class (near background levels) with two more levels in between. Similar to the Richter scale for earthquakes, each of the five levels of letters represents a 10-fold increase in energy output.
The first flare peaked at 5:10 a.m. EDT, while the second, larger flare, peaked at 8:02 a.m. EDT.

Footage of the Sept. 6 X2.2 and X9.3 solar flares captured by the Solar Dynamics Observatory in extreme ultraviolet light (171 angstrom wavelength) with Earth for scale
Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth’s atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however — when intense enough — they can disturb Earth’s atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.
Both Sept. 6 flares erupted from an active region labeled AR 2673. This area also produced a mid-level solar flare on Sept. 4, 2017. This flare peaked at 4:33 p.m. EDT, and was about a tenth the strength of X-class flares like those measured on Sept. 6.

Footage of the Sept. 4 M5.5 solar flare captured by the Solar Dynamics Observatory in extreme ultraviolet light (131 angstrom wavelength)
This active region continues to produce significant solar flares. There were two flares on the morning of Sept. 7 as well.
For the latest updates and to see how these events may affect Earth, please visit NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, the U.S. government’s official source for space weather forecasts, alerts, watches and warnings.
Follow @NASASun on Twitter and NASA Sun Science on Facebook to keep up with all the latest in space weather research.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 b4kafterijay reblogged this · 1 month ago
b4kafterijay reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 deathrattleandroll liked this · 2 months ago
deathrattleandroll liked this · 2 months ago -
 gimmemo618 liked this · 5 months ago
gimmemo618 liked this · 5 months ago -
 annafx0bf liked this · 7 months ago
annafx0bf liked this · 7 months ago -
 zibaldone-di-pensieri liked this · 10 months ago
zibaldone-di-pensieri liked this · 10 months ago -
 craftyahgaseg7 liked this · 10 months ago
craftyahgaseg7 liked this · 10 months ago -
 falcemartello liked this · 10 months ago
falcemartello liked this · 10 months ago -
 seinverno reblogged this · 10 months ago
seinverno reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 kssador liked this · 1 year ago
kssador liked this · 1 year ago -
 master-t liked this · 1 year ago
master-t liked this · 1 year ago -
 marionnjoya reblogged this · 1 year ago
marionnjoya reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 tobeeclectic reblogged this · 1 year ago
tobeeclectic reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 tobeeclectic liked this · 1 year ago
tobeeclectic liked this · 1 year ago -
 master-t reblogged this · 1 year ago
master-t reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 aelffy reblogged this · 1 year ago
aelffy reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 real-fiktcion reblogged this · 1 year ago
real-fiktcion reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 namahalameri liked this · 1 year ago
namahalameri liked this · 1 year ago -
 fuschiah reblogged this · 1 year ago
fuschiah reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 artpronin-blog liked this · 1 year ago
artpronin-blog liked this · 1 year ago -
 magicalbrainepisodes reblogged this · 1 year ago
magicalbrainepisodes reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 nadezhdaventsova liked this · 1 year ago
nadezhdaventsova liked this · 1 year ago -
 chaiberry liked this · 1 year ago
chaiberry liked this · 1 year ago -
 varsiteeclvb liked this · 1 year ago
varsiteeclvb liked this · 1 year ago -
 catennifarmza liked this · 1 year ago
catennifarmza liked this · 1 year ago -
 cherrylvsstuff liked this · 1 year ago
cherrylvsstuff liked this · 1 year ago -
 book-ladder liked this · 1 year ago
book-ladder liked this · 1 year ago -
 cosmostar liked this · 2 years ago
cosmostar liked this · 2 years ago -
 daisy-source liked this · 2 years ago
daisy-source liked this · 2 years ago -
 by-noura liked this · 2 years ago
by-noura liked this · 2 years ago