“Força Eletrostática é Aquela Que Governa O Movimento Dos átomos. É A Força Que Os Faz Colidir
“Força eletrostática é aquela que governa o movimento dos átomos. É a força que os faz colidir e desenvolver a energia de sustentação da vida de calor e luz, e que os faz se agregar em uma variedade infinita de maneiras, de acordo com os designs fantasiosos da Natureza, e formar todas essas estruturas maravilhosas que vemos ao nosso redor . É, de fato, se nossas visões atuais forem verdadeiras, a força mais importante que devemos considerar na Natureza. ” Nikola Tesla
“Electrostatic force is that which governs the motion of the atoms. It is the force which causes them to collide and develop the life-sustaining energy of heat and light, and which causes them to aggregate in an infinite variety of ways, according to Nature’s fanciful designs, and forms all these wondrous structures we see around us. It is, in fact, if our present views be true, the most important force for us to consider in Nature.”
–Nikola Tesla
“Tesla, Marvel Of The Future.” Brooklyn Citizen, August 22, 1897.

More Posts from Ritasakano and Others
As imagens de Júpiter deixa-nos atordoado.

The cloudscape of Jupiter, observed by NASA’s Voyager 1 probe on February 3, 1979.
(Planetary Society)
Orion e a explosão de uma estrela.

ALMA views a stellar explosion in Orion
Stellar explosions are most often associated with supernovae, the spectacular deaths of stars. But new ALMA observations of the Orion Nebula complex provide insights into explosions at the other end of the stellar life cycle, star birth. Astronomers captured these dramatic images of the remains of a 500-year-old explosion as they explored the firework-like debris from the birth of a group of massive stars, demonstrating that star formation can be a violent and explosive process too.
The colours in the ALMA data represent the relative Doppler shifting of the millimetre-wavelength light emitted by carbon monoxide gas. The blue colour in the ALMA data represents gas approaching at the highest speeds; the red colour is from gas moving toward us more slowly.
The background image includes optical and near-infrared imaging from both the Gemini South and ESO Very Large Telescope. The famous Trapezium Cluster of hot young stars appears towards the bottom of this image. The ALMA data do not cover the full image shown here.
Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), J. Bally/H. Drass et al.
Assustador!!
How Do Hurricanes Form?
Hurricanes are the most violent storms on Earth. People call these storms by other names, such as typhoons or cyclones, depending on where they occur.

The scientific term for ALL of these storms is tropical cyclone. Only tropical cyclones that form over the Atlantic Ocean or eastern and central Pacific Ocean are called “hurricanes.”

Whatever they are called, tropical cyclones all form the same way.
Tropical cyclones are like giant engines that use warm, moist air as fuel. That is why they form only over warm ocean waters near the equator. This warm, moist air rises and condenses to form clouds and storms.

As this warmer, moister air rises, there’s less air left near the Earth’s surface. Essentially, as this warm air rises, this causes an area of lower air pressure below.

This starts the ‘engine’ of the storm. To fill in the low pressure area, air from surrounding areas with higher air pressure pushes in. That “new” air near the Earth’s surface also gets heated by the warm ocean water so it also gets warmer and moister and then it rises.

As the warm air continues to rise, the surrounding air swirls in to take its place. The whole system of clouds and wind spins and grows, fed by the ocean’s heat and water evaporating from the surface.
As the storm system rotates faster and faster, an eye forms in the center. It is vey calm and clear in the eye, with very low air pressure.

Tropical cyclones usually weaken when they hit land, because they are no longer being “fed” by the energy from the warm ocean waters. However, when they move inland, they can drop many inches of rain causing flooding as well as wind damage before they die out completely.
There are five types, or categories, of hurricanes. The scale of categories is called the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale and they are based on wind speed.

How Does NASA Study Hurricanes?
Our satellites gather information from space that are made into pictures. Some satellite instruments measure cloud and ocean temperatures. Others measure the height of clouds and how fast rain is falling. Still others measure the speed and direction of winds.

We also fly airplanes into and above hurricanes. The instruments aboard planes gather details about the storm. Some parts are too dangerous for people to fly into. To study these parts, we use airplanes that operate without people.
To learn more about how we study hurricanes, visit: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hurricanes/main/index.html
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
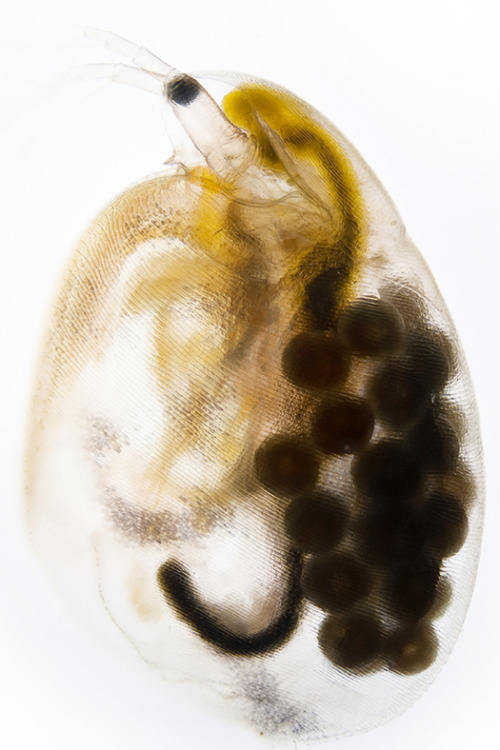
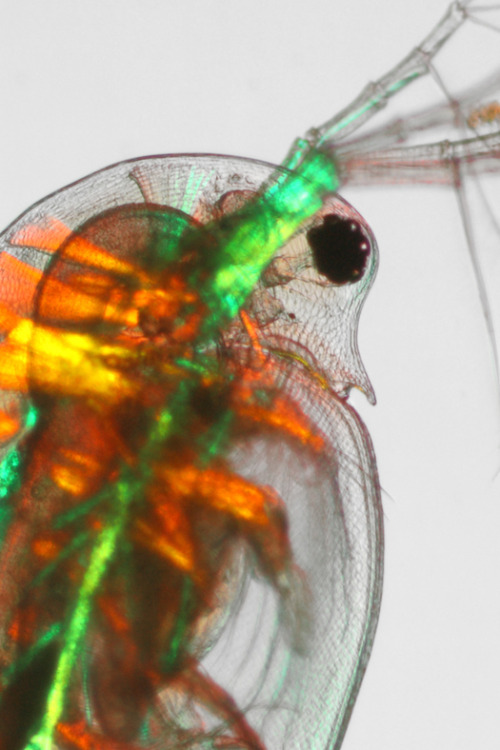
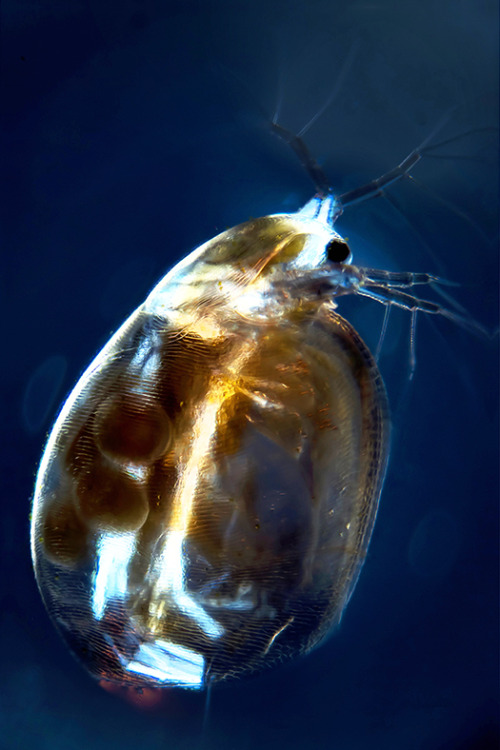


A salty situation.
Zooplankton may be the smallest species in the freshwater food chain, but they play a big role in preserving our lakes, streams and wetlands. That’s one of the reasons why IBM joined forces with the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and The FUND for Lake George to create the Jefferson Project at Lake George to understand and protect freshwater ecosystems. Recently they studied the effects road salt has on a species of zooplankton. Road salt usage has increased 50-fold since 1940, and bodies of freshwater are increasing in salinity because of it. Using IBM technology, the researchers monitored zooplankton in varying levels of salinity and found that the organisms were capable of evolving a higher tolerance to the salt. This is good news for the ecosystem since the loss of plankton could have cascading effects throughout the food chain. See, small can be mighty too.
Explore the study’s results →

Primeira flor de Pêssego Ao vento frio de final de março Um desassossego Na alma O começo.
“Pauta do Congresso agora é vingança contra MP e Judiciário”, diz procurador - O Antagonista
Onde as árvores falam.





清水寺ーSEISUIJI * 佐渡にあるお寺 誰もいなくて冷んやりしてて でもすごく懐かしい場所だった
-
 brokebutstillrich liked this · 2 years ago
brokebutstillrich liked this · 2 years ago -
 smm800 reblogged this · 3 years ago
smm800 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 smm800 liked this · 3 years ago
smm800 liked this · 3 years ago -
 dreaminexe liked this · 3 years ago
dreaminexe liked this · 3 years ago -
 lovee-pdf reblogged this · 4 years ago
lovee-pdf reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 zainaljanabi liked this · 4 years ago
zainaljanabi liked this · 4 years ago -
 topphotography liked this · 4 years ago
topphotography liked this · 4 years ago -
 amos8888 liked this · 4 years ago
amos8888 liked this · 4 years ago -
 mothersasha reblogged this · 4 years ago
mothersasha reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 jlmae liked this · 4 years ago
jlmae liked this · 4 years ago -
 torken980 liked this · 4 years ago
torken980 liked this · 4 years ago -
 lady-loves-a-lot liked this · 4 years ago
lady-loves-a-lot liked this · 4 years ago -
 robdawg098 liked this · 4 years ago
robdawg098 liked this · 4 years ago -
 gabbieborghini reblogged this · 4 years ago
gabbieborghini reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 lilacvoidinthesky liked this · 4 years ago
lilacvoidinthesky liked this · 4 years ago -
 jaymz469 liked this · 4 years ago
jaymz469 liked this · 4 years ago -
 bearranger11 liked this · 4 years ago
bearranger11 liked this · 4 years ago -
 blackworra reblogged this · 4 years ago
blackworra reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 ssugwn liked this · 4 years ago
ssugwn liked this · 4 years ago -
 schizo-eye reblogged this · 4 years ago
schizo-eye reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 schizo-eye liked this · 4 years ago
schizo-eye liked this · 4 years ago -
 andrea-wreaks-havoc reblogged this · 4 years ago
andrea-wreaks-havoc reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 bohemotash liked this · 4 years ago
bohemotash liked this · 4 years ago -
 dworkin-disciple reblogged this · 4 years ago
dworkin-disciple reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 rarelement reblogged this · 4 years ago
rarelement reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 dyingbreed79 reblogged this · 4 years ago
dyingbreed79 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 dyingbreed79 liked this · 4 years ago
dyingbreed79 liked this · 4 years ago -
 watch-out-idiot-passing-through reblogged this · 4 years ago
watch-out-idiot-passing-through reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 watch-out-idiot-passing-through liked this · 4 years ago
watch-out-idiot-passing-through liked this · 4 years ago -
 science-child reblogged this · 4 years ago
science-child reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 baron-amaro liked this · 4 years ago
baron-amaro liked this · 4 years ago -
 gknnkvgcjvjuubbubyb-blog liked this · 4 years ago
gknnkvgcjvjuubbubyb-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 jesusknowsaboutyouchange liked this · 4 years ago
jesusknowsaboutyouchange liked this · 4 years ago -
 166624 reblogged this · 4 years ago
166624 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 166624 liked this · 4 years ago
166624 liked this · 4 years ago -
 inthemirrordorkly liked this · 4 years ago
inthemirrordorkly liked this · 4 years ago