Science-is-magical - Science Is Magic

More Posts from Science-is-magical and Others
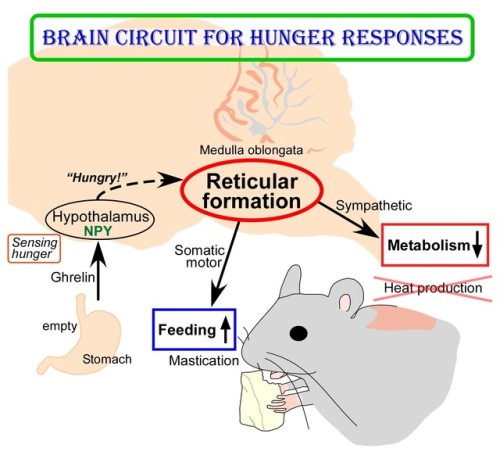
(Image caption: The empty stomach releases the hormone called ghrelin. By receiving ghrelin, the hypothalamus in the brain senses hunger and produces “hunger signaling” through the action of neuropeptide Y (NPY). The hunger signaling activates neurons in the reticular formation of the medulla oblongata, which then inhibit sympathetic output to reduce metabolic heat production and simultaneously provide masticatory motor rhythm to facilitate feeding. Credit: © 2017 Yoshiko Nakamura)
New Insights into Brain Circuit for Hunger Responses during Starvation
The human body responds to starving conditions, such as famine, to promote the chance of survival. It reduces energy expenditure by stopping heat production and promotes feeding behavior. These “hunger responses” are activated by the feeling of hunger in the stomach and are controlled by neuropeptide Y (NPY) signals released by neurons in the hypothalamus. However, how NPY signaling in the hypothalamus elicits the hunger responses has remained unknown.
Sympathetic motor neurons in the medulla oblongata are responsible for heat production by brown adipose tissue (BAT). Researchers centered at Nagoya University have now tested whether the heat-producing neurons respond to the same hypothalamic NPY signals that control hunger responses. They injected NPY into the hypothalamus of rats and tested the effect on heat production. Under normal conditions, blocking inhibitory GABAergic receptors or stimulating excitatory glutamatergic receptors in the sympathetic motor neurons induced heat production in BAT. After NPY injection, stimulating glutamatergic receptors did not produce heat, but inhibiting GABAergic receptors did. The study was reported in Cell Metabolism.
“This indicated that hypothalamic NPY signals prevent BAT thermogenesis by using inhibitory GABAergic inputs to sympathetic motor neurons,” study lead author Yoshiko Nakamura says.
Retrograde and anterograde tracing with fluorescent dyes revealed which brain region provided the inhibitory GABAergic inputs to heat-producing motor neurons.
“Tracing experiments showed that sympathetic motor neurons are directly innervated by GABAergic inputs from reticular nuclei in the medulla oblongata,” corresponding author Kazuhiro Nakamura explains, “selective activation of these GABAergic reticular neurons inhibits BAT thermogenesis.”
The researchers’ further findings showed that GABAergic inputs from medullary reticular neurons are involved in hypothalamic NPY-mediated inhibition of heat production in BAT. This hunger response circuit probably explains why anorexic individuals suffer from hypothermia.
Interestingly, stimulation of these medullary reticular neurons prompted rats to begin chewing and feeding. This effect was similar to injecting NPY into the hypothalamus, suggesting that hypothalamic NPY signaling activates reticular neurons in the medulla oblongata to promote feeding and mastication during the hunger response.
Abnormal activation of these neurons under non-starved conditions may contribute to obesity. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to development of more effective treatments for obesity.




TYPES OF COLOR-BLINDNESS
1. Normal vision
2. Deuteranopia
3. Tritanopia
4. Monochromacy - An extremely rare type of color-blindness in which sufferers can see only in shades of grey, and perceive no color at all. About 1 in 33,000 people is born with this condition.
(Source)

I am not going to tag the name of the bird, because I’m pretty sure I would get tagged as NSFW if I did, but I assure you their beaks are getting longer and it’s probably because of the UK’s obsession with bird feeders.

Israeli scientists see breakthrough in AIDS cure
Drug now being tested causes HIV-infected cells to self-destruct without harming the rest of the body
BY
TIMES OF ISRAEL STAFF
November 1, 2016, 3:26 am
HIV and AIDS patients may find new hope in a drug developed at Hebrew University in Jerusalem which is currently being tested at the Kaplan Medical Center in Rehovot.
The drug was inserted into test tubes containing the blood of ten AIDS patients currently being treated at the hospital, and was found to decrease the HIV virus count in the blood samples by as much as 97 percent in just eight days, Channel 2 reported Monday.
The active ingredient in the drug is a peptide, or smaller version of a protein, that was developed by Abraham Loyter and Assaf Friedler at Hebrew University. The peptide causes several copies of the virus’s DNA to enter the infected cell, instead of just one copy, causing the cell to self-destruct.
HIV is currently treated with a cocktail of drugs that slow the progression of the infection in the body but never rid the patient of the virus entirely. These drugs have allowed doctors to treat AIDS as a chronic illness as opposed to a fatal one.
Loyter explained that the new approach is superior to previous efforts.
“With our approach,” Loyter told Channel 2, “we are destroying the cells, so there is no chance that the virus will awaken one day, because there are no cells, there will be no cells that contain the virus.”
Loyter explained that “the drug enhances certain processes in the body during the spreading of the virus and that enhancement kills certain cells.”
In a separate but related development, the Health Ministry announced last week it would begin distributing prophylactic drugs for the first time to populations at higher risk of contracting HIV. The drugs, when taken regularly, have been found to be effective in preventing the spread of HIV during contact.
Contamination-seeking drones - IBM Patent 9447448.
Stay back and let the drones do the dirty work. Patent 9447448 makes cognitive drones able to inspect and decontaminate places so humans don’t have to. The drones’ on-board AI system can collect and analyze samples, so it can identify and clean up any bacteria or outbreak. Meanwhile you get to hang back, safely out of harm’s way.
This is just one of the record-breaking 8,000+ patents IBM received this year. Explore the latest IBM patents. →
-
 zebravalis liked this · 1 year ago
zebravalis liked this · 1 year ago -
 blushshop liked this · 1 year ago
blushshop liked this · 1 year ago -
 thanktideroxi liked this · 1 year ago
thanktideroxi liked this · 1 year ago -
 proxyrse liked this · 2 years ago
proxyrse liked this · 2 years ago -
 grimmseraph reblogged this · 2 years ago
grimmseraph reblogged this · 2 years ago