Undulatus Asperatus



Undulatus asperatus
Undulatus asperatus is a new separate cloud classification currently on petition to be added to the official list of observable cloud types. If accepted as a distinct cloud type, it will be the first addition to the list of cloud types since cirrus intortus was added in 1951. It was proposed by the founder of The Cloud Appreciation Society. Recognition of the cloud classification is still pending.
The experience of these clouds is as if, it is said, one were below the Sea looking up at the surface of the water. Yet when they occur, there reportedly is little to no turbulence at the land surface. The clouds are most common in the Great Plains of the United States following thunderstorm activity in the earlier parts of the day.
More Posts from Sidusglacies and Others

Where clouds form. Understanding Our World. Book 2. 1947. Internet Archive

新幹線と富士山 (via かがみ~)

For more than a century, scientists have been fascinated by the jet that forms after a drop impacts a liquid. In this study, researchers tracked fluorescent particles in the fluid to understand the velocity and acceleration of flow inside the jet. (Image and research credit: C. van Rijn et al.; via APS Physics; submitted by Kam-Yung Soh)

https://www.instagram.com/p/BIGb_knD77X/






- space;the physical universe beyond the earth’s atmosphere//mod carter




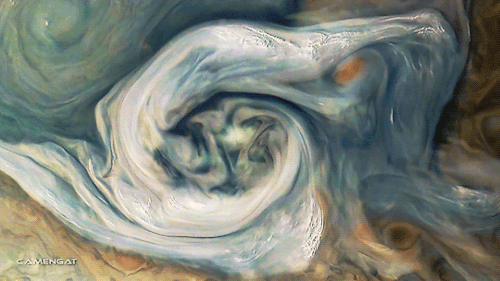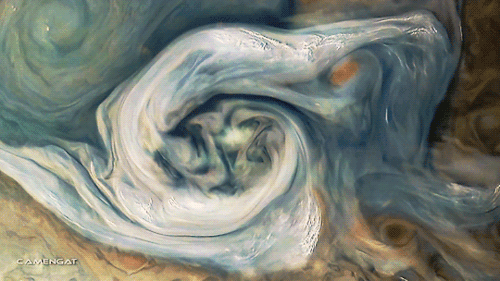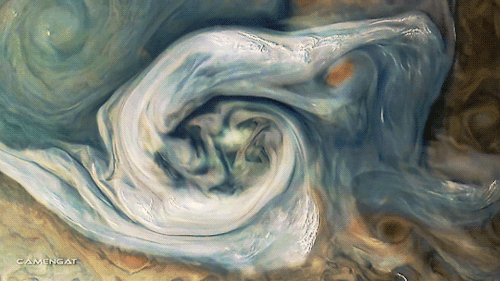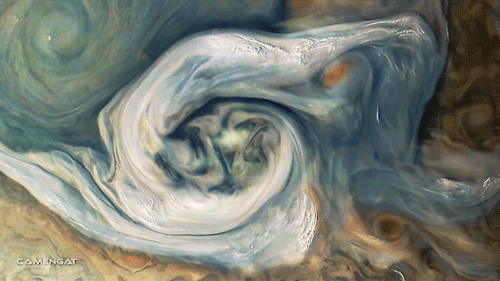





Planet: Jupiter

Polar Vortex Disruption Of January 2013
Satellite imagery of the disruption of the polar vortex in the northern hemisphere winter 2012-2013. The data show a major stratospheric sudden warming (SSW) event, linked to the distortion and reversal of the normal westerly (moving west to east) flow of air.
The large vortex (bright) over the North Atlantic Ocean at the start of the clip breaks up into several smaller vortices. This is due to air from lower latitudes (dark) becoming entrained in the polar flow, forming an anti-cyclonic region (dark, rotating clockwise) over Japan and eastern Russia, which disrupts the flow across the region.
Learn More About The Polar Vortex
Although dramatic, such events are not rare, occurring every two years on average. They can cause winds to reverse near the surface too, leading to very cold spells, especially in North America and Europe.
The brightness indicates the potential vorticity of the air, a measure of its rotation within its flow, at an altitude of 35 kilometers. Brighter regions have more vorticity.
A major SSW occurs when the temperatures in the stratosphere around the pole increases by at least 25 Kelvin within a week, causing the wind to change direction.
The data were gathered by the GEOS-5 satellite every hour between 15th December 2012 and 28th January 2013.
© GMAO / GSFC / NASA / Science Source









“Using nothing more than Newton’s laws of gravitation, we astronomers can confidently predict that several billion years from now, our home galaxy, the Milky Way, will merge with our neighboring galaxy Andromeda. Because the distances between the stars are so great compared to their sizes, few if any stars in either galaxy will actually collide.
Any life on the worlds of that far-off future should be safe, but they would be treated to an amazing, billion-year-long light show a dance of a half a trillion stars to music first heard on one little world by a man who had but one true friend.”
COSMOS: A Spacetime Odyssey (2014) written by Ann Druyan and Steven Soter
-
 sh-aimlessly reblogged this · 2 years ago
sh-aimlessly reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 asexyclown liked this · 4 years ago
asexyclown liked this · 4 years ago -
 sidusglacies reblogged this · 4 years ago
sidusglacies reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 boyist liked this · 4 years ago
boyist liked this · 4 years ago -
 kernelstation reblogged this · 4 years ago
kernelstation reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 kernelstation liked this · 4 years ago
kernelstation liked this · 4 years ago -
 110car8s liked this · 4 years ago
110car8s liked this · 4 years ago -
 the-smallest-mew reblogged this · 4 years ago
the-smallest-mew reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 the-smallest-mew liked this · 4 years ago
the-smallest-mew liked this · 4 years ago -
 yamelcakes reblogged this · 4 years ago
yamelcakes reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 almamiaamaelcafe liked this · 4 years ago
almamiaamaelcafe liked this · 4 years ago -
 gabbygabth liked this · 5 years ago
gabbygabth liked this · 5 years ago -
 hypacia liked this · 5 years ago
hypacia liked this · 5 years ago -
 umberowl liked this · 5 years ago
umberowl liked this · 5 years ago -
 catcabritto reblogged this · 6 years ago
catcabritto reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 catcabritto liked this · 6 years ago
catcabritto liked this · 6 years ago -
 jannamk792 reblogged this · 6 years ago
jannamk792 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 saltrosegold liked this · 6 years ago
saltrosegold liked this · 6 years ago -
 not2late4notes reblogged this · 6 years ago
not2late4notes reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 not2late liked this · 6 years ago
not2late liked this · 6 years ago -
 andreanoreply reblogged this · 6 years ago
andreanoreply reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 syahsex liked this · 6 years ago
syahsex liked this · 6 years ago -
 jannamk792 reblogged this · 7 years ago
jannamk792 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 jannamk792 liked this · 7 years ago
jannamk792 liked this · 7 years ago -
 takeheartsweetheart reblogged this · 7 years ago
takeheartsweetheart reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 spaceprincessblog-blog liked this · 7 years ago
spaceprincessblog-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 drum61-blog liked this · 7 years ago
drum61-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 gillipea liked this · 7 years ago
gillipea liked this · 7 years ago -
 the-worst-at-everything reblogged this · 7 years ago
the-worst-at-everything reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 deerbot36 reblogged this · 7 years ago
deerbot36 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 deerbot36 liked this · 7 years ago
deerbot36 liked this · 7 years ago -
 gwyvian reblogged this · 7 years ago
gwyvian reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 gwyvian liked this · 7 years ago
gwyvian liked this · 7 years ago -
 noches-sin-lunas-blog liked this · 7 years ago
noches-sin-lunas-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 stealth-science reblogged this · 7 years ago
stealth-science reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 accas-and-raucous reblogged this · 7 years ago
accas-and-raucous reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 mesocyclonic reblogged this · 7 years ago
mesocyclonic reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 daddy-daichis reblogged this · 7 years ago
daddy-daichis reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 rocanono reblogged this · 7 years ago
rocanono reblogged this · 7 years ago








