Claude Monet’s Water Structure And Shades, II, Transparent Single Picture Version.

Claude Monet’s water structure and shades, II, transparent single picture version.
More Posts from Sidusglacies and Others

“One of the most actively changing areas on Mars are the steep edges of the North Polar layered deposits. This image from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows many new ice blocks compared to an earlier image in December 2006. An animation shows one example, where a section of ice cliff collapsed. The older image (acquired in bin-2 mode) is not as sharp as the newer one.” Credit - nasa.gov


A Tour of Storms Across the Solar System

Earth is a dynamic and stormy planet with everything from brief, rumbling thunderstorms to enormous, raging hurricanes, which are some of the most powerful and destructive storms on our world. But other planets also have storm clouds, lightning — even rain, of sorts. Let’s take a tour of some of the unusual storms in our solar system and beyond.
Tune in May 22 at 3 p.m. for more solar system forecasting with NASA Chief Scientist Jim Green during the latest installment of NASA Science Live: https://www.nasa.gov/nasasciencelive.

1. At Mercury: A Chance of Morning Micrometeoroid Showers and Magnetic ‘Tornadoes’
Mercury, the planet nearest the Sun, is scorching hot, with daytime temperatures of more than 800 degrees Fahrenheit (about 450 degrees Celsius). It also has weak gravity — only about 38% of Earth’s — making it hard for Mercury to hold on to an atmosphere.
Its barely there atmosphere means Mercury doesn’t have dramatic storms, but it does have a strange “weather” pattern of sorts: it’s blasted with micrometeoroids, or tiny dust particles, usually in the morning. It also has magnetic “tornadoes” — twisted bundles of magnetic fields that connect the planet’s magnetic field to space.

2. At Venus: Earth’s ‘Almost’ Twin is a Hot Mess
Venus is often called Earth’s twin because the two planets are similar in size and structure. But Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system, roasting at more than 800 degrees Fahrenheit (430 degrees Celsius) under a suffocating blanket of sulfuric acid clouds and a crushing atmosphere. Add to that the fact that Venus has lightning, maybe even more than Earth.
In visible light, Venus appears bright yellowish-white because of its clouds. Earlier this year, Japanese researchers found a giant streak-like structure in the clouds based on observations by the Akatsuki spacecraft orbiting Venus.

3. At Earth: Multiple Storm Hazards Likely
Earth has lots of storms, including thunderstorms, blizzards and tornadoes. Tornadoes can pack winds over 300 miles per hour (480 kilometers per hour) and can cause intense localized damage.
But no storms match hurricanes in size and scale of devastation. Hurricanes, also called typhoons or cyclones, can last for days and have strong winds extending outward for 675 miles (1,100 kilometers). They can annihilate coastal areas and cause damage far inland.

4. At Mars: Hazy with a Chance of Dust Storms
Mars is infamous for intense dust storms, including some that grow to encircle the planet. In 2018, a global dust storm blanketed NASA’s record-setting Opportunity rover, ending the mission after 15 years on the surface.
Mars has a thin atmosphere of mostly carbon dioxide. To the human eye, the sky would appear hazy and reddish or butterscotch colored because of all the dust suspended in the air.

5. At Jupiter: A Shrinking Icon
It’s one of the best-known storms in the solar system: Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. It’s raged for at least 300 years and was once big enough to swallow Earth with room to spare. But it’s been shrinking for a century and a half. Nobody knows for sure, but it’s possible the Great Red Spot could eventually disappear.

6. At Saturn: A Storm Chasers Paradise
Saturn has one of the most extraordinary atmospheric features in the solar system: a hexagon-shaped cloud pattern at its north pole. The hexagon is a six-sided jet stream with 200-mile-per-hour winds (about 322 kilometers per hour). Each side is a bit wider than Earth and multiple Earths could fit inside. In the middle of the hexagon is what looks like a cosmic belly button, but it’s actually a huge vortex that looks like a hurricane.
Storm chasers would have a field day on Saturn. Part of the southern hemisphere was dubbed “Storm Alley” by scientists on NASA’s Cassini mission because of the frequent storm activity the spacecraft observed there.

7. At Titan: Methane Rain and Dust Storms
Earth isn’t the only world in our solar system with bodies of liquid on its surface. Saturn’s moon Titan has rivers, lakes and large seas. It’s the only other world with a cycle of liquids like Earth’s water cycle, with rain falling from clouds, flowing across the surface, filling lakes and seas and evaporating back into the sky. But on Titan, the rain, rivers and seas are made of methane instead of water.
Data from the Cassini spacecraft also revealed what appear to be giant dust storms in Titan’s equatorial regions, making Titan the third solar system body, in addition to Earth and Mars, where dust storms have been observed.

8. At Uranus: A Polar Storm
Scientists were trying to solve a puzzle about clouds on the ice giant planet: What were they made of? When Voyager 2 flew by in 1986, it spotted few clouds. (This was due in part to the thick haze that envelops the planet, as well as Voyager’s cameras not being designed to peer through the haze in infrared light.) But in 2018, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope snapped an image showing a vast, bright, stormy cloud cap across the north pole of Uranus.

9. At Neptune: Methane Clouds
Neptune is our solar system’s windiest world. Winds whip clouds of frozen methane across the ice giant planet at speeds of more than 1,200 miles per hour (2,000 kilometers per hour) — about nine times faster than winds on Earth.
Neptune also has huge storm systems. In 1989, NASA’s Voyager 2 spotted two giant storms on Neptune as the spacecraft zipped by the planet. Scientists named the storms “The Great Dark Spot” and “Dark Spot 2.”

10. It’s Not Just Us: Extreme Weather in Another Solar System
Scientists using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope made a global map of the glow from a turbulent planet outside our solar system. The observations show the exoplanet, called WASP-43b, is a world of extremes. It has winds that howl at the speed of sound, from a 3,000-degree-Fahrenheit (1,600-degree-Celsius) day side, to a pitch-black night side where temperatures plunge below 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit (500 degrees Celsius).
Discovered in 2011, WASP-43b is located 260 light-years away. The planet is too distant to be photographed, but astronomers detected it by observing dips in the light of its parent star as the planet passes in front of it.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.









Do Earth-Sized Planets Around Other Stars Have Atmospheres? James Webb Will Find Out!
“Even so, because of its ability to measure light to high sensitivity far into the infrared, there’s a remarkable hope for determining whether these worlds have atmosphere regardless of any other measurements. As planets orbit their star, we see different phases: a full phase when it’s on the far side of the star; a new phase when it’s on the near side, and everything in between. Based on the temperature of the world at night, we’ll receive different amounts of infrared light from the "dark” side that faces away from the Sun. Even without a transit, James Webb should be able to measure this.“
The overwhelming majority of Earth-sized, potentially habitable planets that Kepler found are in orbit around red dwarf stars. In many ways, this is great: red dwarf stars are stable, temperature-wise, for longer than our Sun. Their planets are easier to detect, and they will be the first Earth-sized ones we can measure the atmospheres of directly. But even if we can’t make those measurements with James Webb, we’ll be able to learn whether they have atmospheres or not via a different method: by measuring the infrared radiation coming from the planets themselves in various phases. Just as we can measure the presence of Venus’ atmosphere from the hot, infrared radiation emanating from it even on the night side, we can make those same measurements with James Webb of other Solar Systems. By time the early 2020s roll around, we’ll have our first answers to this longstanding debate.
Many scientists think that Earth-sized planets around M-class stars will have no atmospheres left; others think there’s a chance they survive. Here’s how James Webb will find out!
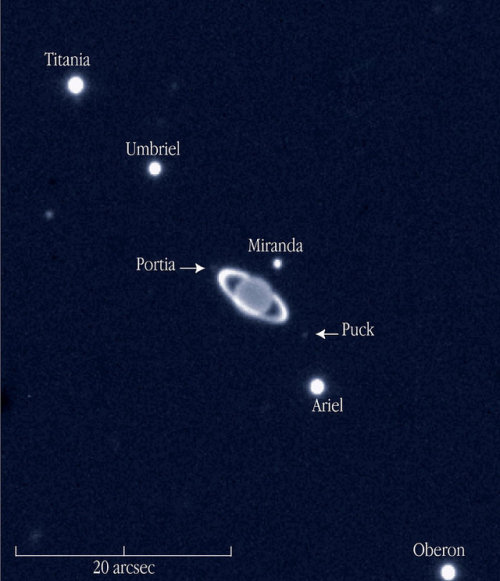
A near-infrared view of the giant planet Uranus with rings and some of its moons, obtained on November 19, 2002, with the ISAAC multi-mode instrument on the 8.2-m VLT ANTU telescope at the ESO Paranal Observatory (Chile). The moons are identified; the unidentified, round object to the left is a background star. The image scale in indicated by the bar.
Credit: ESO


What is this dark spot in the center of the image?
This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image features the star cluster Trumpler 14. One of the largest gatherings of hot, massive and bright stars in the Milky Way, this cluster houses some of the most luminous stars in our entire galaxy.
The prominent dark patch, close to the centre of the cluster is a so called Bok globule: this is an isolated and relatively small dark nebula, containing dense dust and gas. These objects are still subjects of intense research as their structure and density remains somewhat a mystery.
Credit: NASA & ESA, Jesús Maíz Apellániz (Centro de Astrobiología, CSIC-INTA, Spain)
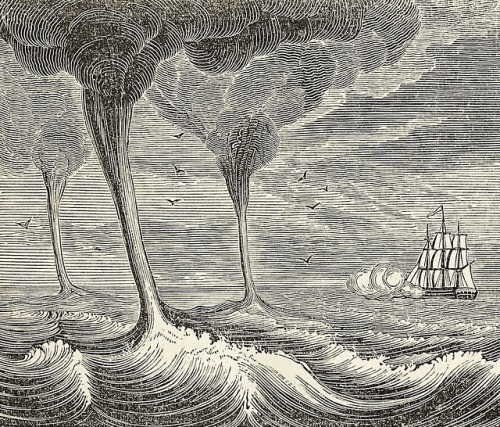


The philosophy of storms - James Pollard Espy - 1841 - via Internet Archive

Retrograde motion of Mars in the night sky of the Earth.
Image Credit: Tunc Tezel
-
 artandallitsfacets reblogged this · 1 month ago
artandallitsfacets reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 steliosagapitos reblogged this · 1 month ago
steliosagapitos reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 steliosagapitos liked this · 1 month ago
steliosagapitos liked this · 1 month ago -
 littoboepeep liked this · 1 month ago
littoboepeep liked this · 1 month ago -
 internetthug reblogged this · 1 month ago
internetthug reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 internetthug liked this · 1 month ago
internetthug liked this · 1 month ago -
 sabjetm reblogged this · 2 months ago
sabjetm reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 dreammybeat reblogged this · 3 months ago
dreammybeat reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 mrdchwlgry liked this · 4 months ago
mrdchwlgry liked this · 4 months ago -
 f0und-the-devil-in-me liked this · 5 months ago
f0und-the-devil-in-me liked this · 5 months ago -
 fadingcreatorpainter liked this · 6 months ago
fadingcreatorpainter liked this · 6 months ago -
 bossboudicca liked this · 6 months ago
bossboudicca liked this · 6 months ago -
 jonairadreaming reblogged this · 6 months ago
jonairadreaming reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 thiddyswife reblogged this · 6 months ago
thiddyswife reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 thiddyswife liked this · 6 months ago
thiddyswife liked this · 6 months ago -
 aquatixwitch reblogged this · 6 months ago
aquatixwitch reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 11-september-1996 liked this · 7 months ago
11-september-1996 liked this · 7 months ago -
 lunamond liked this · 7 months ago
lunamond liked this · 7 months ago -
 crystalthevampirate liked this · 7 months ago
crystalthevampirate liked this · 7 months ago -
 strike-another-match reblogged this · 7 months ago
strike-another-match reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 jonairadreaming liked this · 8 months ago
jonairadreaming liked this · 8 months ago -
 vhagar-balerion-meraxes liked this · 8 months ago
vhagar-balerion-meraxes liked this · 8 months ago -
 playlistashton liked this · 8 months ago
playlistashton liked this · 8 months ago -
 playlistashton reblogged this · 8 months ago
playlistashton reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 disaster-j reblogged this · 8 months ago
disaster-j reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 disaster-j liked this · 8 months ago
disaster-j liked this · 8 months ago -
 ahysopae reblogged this · 8 months ago
ahysopae reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 snappyjackstuff liked this · 8 months ago
snappyjackstuff liked this · 8 months ago -
 ahysopae liked this · 8 months ago
ahysopae liked this · 8 months ago -
 kuraioshiro reblogged this · 8 months ago
kuraioshiro reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 indulgeinluxuries reblogged this · 9 months ago
indulgeinluxuries reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 sablaveritable reblogged this · 9 months ago
sablaveritable reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 sablaveritable liked this · 9 months ago
sablaveritable liked this · 9 months ago -
 lilianaarch liked this · 9 months ago
lilianaarch liked this · 9 months ago -
 mybrotherstolemyquesadilla reblogged this · 9 months ago
mybrotherstolemyquesadilla reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 starlite-bunny liked this · 10 months ago
starlite-bunny liked this · 10 months ago -
 honeyandthunderstorms reblogged this · 10 months ago
honeyandthunderstorms reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 honeyandthunderstorms liked this · 10 months ago
honeyandthunderstorms liked this · 10 months ago -
 formulaocean reblogged this · 10 months ago
formulaocean reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 asstheticbinch reblogged this · 10 months ago
asstheticbinch reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 i-just-love-sweaters reblogged this · 10 months ago
i-just-love-sweaters reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 i-just-love-sweaters liked this · 10 months ago
i-just-love-sweaters liked this · 10 months ago -
 crabfin reblogged this · 10 months ago
crabfin reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 crabfin liked this · 10 months ago
crabfin liked this · 10 months ago -
 konfuziusmcpoop reblogged this · 10 months ago
konfuziusmcpoop reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 kimchi-cat reblogged this · 10 months ago
kimchi-cat reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 mokeonn liked this · 10 months ago
mokeonn liked this · 10 months ago -
 mybrotherstolemyquesadilla liked this · 10 months ago
mybrotherstolemyquesadilla liked this · 10 months ago
