If You Couldn’t Tell Already, NASA Is Having A Great Year. From Pluto To Food Grown In Space, Even










If you couldn’t tell already, NASA is having a great year. From Pluto to food grown in space, even in the face of budget cuts, the nation’s space agency had some stellar highlights. Most mysteriously of all, a spacecraft found two eerily bright lights on a distant dwarf planet.
More Posts from Space-m17-blog and Others

Aurora from the ISS.
Photo credit: NASA
Sea Level Rise

For thousands of years, sea level has remained relatively stable. But now, Earth’s seas are rising. Since the beginning of the 20th century, they have risen about eight inches, and more than two inches in the last 20 years alone!

As water warms, it expands and takes up more space. That means that when oceans warm, the sea level rises. This summer, we’ve been researching exactly how global warming has impacted Greenland’s ice sheet. Our ICESat-2 mission will use a laser to measure the height of the planet’s surface. Over time, we will be able to provide a record of elevation change, and estimate how much water has melted into the ocean from land ice change.
So how much ice are we actually losing? Great question, but the answer might shock you. In Greenland alone, 303 gigatons of ice was lost in 2014!

Since we know that ice is melting, we’re working to gain a better understanding of how much and how fast. We’re using everything from planes, probes and boats, to satellites and lasers to determine the impact of global warming on the Earth’s ice.

Follow along for updates and information: http://climate.nasa.gov/

The Earth under Saturn’s rings

First time shooting the Perseid meteor shower. Definitely doing this again and I’ll try to get the Geminids in December as well. Finally edited and put these pictures together. This one turned out pretty good I think, I also have some more on my flickr account with better quality. There’s about 40 meteors here, captured from both nights and combined into one. Was up on Mt. Lemmon for both nights and started shooting from midnight to about 4am.

This Monday, Aug. 17, marks the final targeted flyby of Dione, one of Saturn’s many moons, in Cassini’s long mission. During this flyby, the science team will conduct a gravity experiment that will contribute to our knowledge of the internal structure of Dione. We will also learn more about its outer ice shell, and will be able to compare this with Saturn’s other icy moons.
Beyond the icy moons, Saturn is adorned with thousands of beautiful ringlets, While all four gas giant planets in our solar system have rings – made of chunks of ice and rock – none are as spectacular or as complicated as Saturn’s. Like the other gas giants, Saturn is mostly a massive ball of hydrogen and helium.

This image of Saturn was taken using an infrared filter. Using this type of filter can help scientists determine the location of clouds in the planet’s atmosphere. The darker areas reveal clouds that are lower in the atmosphere, while the bright areas are higher altitude clouds.
Since Cassini reached Saturn in 2004, it has captured important data and images. This spacecraft has the ability to “see” in wavelengths that the human eye cannot, and it can “feel” things about magnetic fields and tiny dust particles that no human hand could detect. These heightened “senses” have allowed us to have a better understanding of Saturn, its moons and the solar system.

Learn more about Cassini & Saturn: http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/
Normal Things…Done in a Not So Normal Way
Floating around in zero gravity may sound like a blast, but it can actually present a lot of challenges to things we do everyday here on Earth with little to no thought. Here are a few ways that astronauts on the International Space Station complete normal tasks in orbit:
1) Washing Hair

You can’t just have a shower on the space station because the water would come out of the faucet and float all over the place. In this video, NASA Astronaut Karen Nyberg demonstrates how she uses a bag of water, no rinse shampoo, a towel and her comb to wash her hair.
2) Drinking Coffee

Believe it or not, there are special cups used on the space station to drink coffee from the new ISSpresso machine. I mean, you wouldn’t want hot coffee floating around in the air…would you? Previously, astronauts drank coffee from plastic bags, but let’s face it, that sounds pretty unenjoyable. Now, there are zero Gravity coffee cups, and an Italian espresso machine aboard the International Space Station! These cups were created with the help of capillary flow experiments conducted in space.
3) Sleeping

There’s nothing like crawling into bed after a long day, but astronauts can’t exactly do that while they’re in microgravity. Instead of beds, crew members use sleeping bags attached to the walls of their small crew cabins. They are able to zipper themselves in so that they don’t float around while they’re asleep. This may sound uncomfortable, but some astronauts, like Scott Kelly, say that they sleep better in space than they do on Earth!
4) Exercising

Exercising in general is an important part of a daily routine. In space, it even helps prevent the effects of bone and muscle loss associated with microgravity. Typically, astronauts exercise two hours per day, but the equipment they use is different than here on Earth. For example, if an astronaut wants to run on the treadmill, they have to wear a harness and bungee cords so that they don’t float away.

js

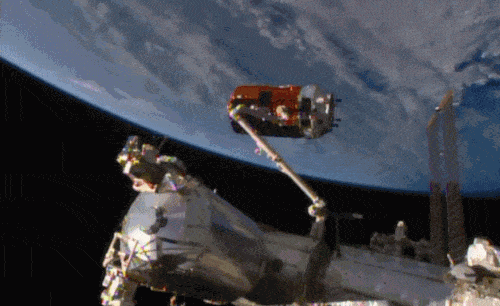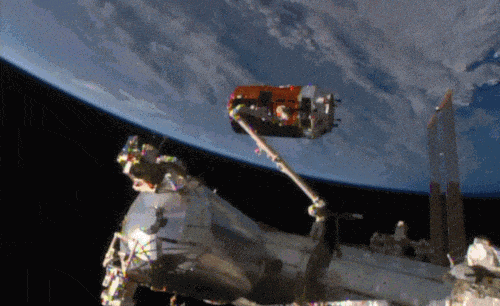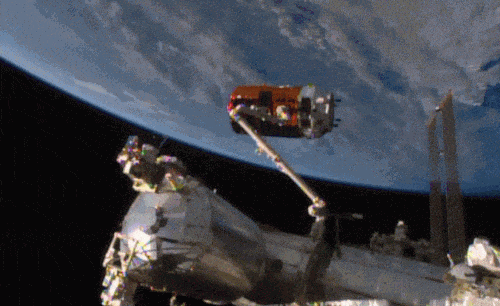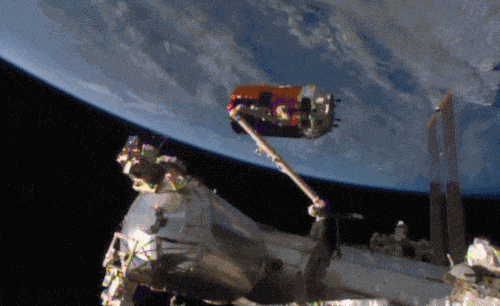
Aboard the International Space Station this morning, Astronaut Kimiya Yui of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) successfully captured JAXA’s Kounotori 5 H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV-5) at 6:28 a.m. EDT.
Yui commanded the station’s robotic arm, Canadarm2, to reach out and grapple the HTV-5, while NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren provided assistance and Scott Kelly monitored HTV-5 systems. The HTV-5 launched aboard an H-IIB rocket at 7:50 a.m. Wednesday, Aug. 19, from the Tanegashima Space Center in southern Japan. Since then, the spacecraft has performed a series of engine burns to fine-tune its course for arrival at the station.
The HTV-5 is delivering more than 8,000 pounds of equipment, supplies and experiments in a pressurized cargo compartment. The unpressurized compartment will deliver the 1,400-pound CALorimetric Electron Telescope (CALET) investigation, an astrophysics mission that will search for signatures of dark matter and provide the highest energy direct measurements of the cosmic ray electron spectrum.
Below is a breathtaking image shared by Astronaut Scott Kelly of the HTV-5 and Canadarm2, which reached out and grappled the cargo spacecraft.

What’s Up for September?

Stargazing and looking up into the night sky is always a fun thing to do. This month, it will be especially exciting because there will be a total eclipse of a supermoon, plus the opportunity to see planets and the late-summer Milky Way!
What is a supermoon?

A supermoon is a new or full moon that occurs when it is at, or near its closest approach to Earth in a given orbit. There are usually 4 to 6 supermoons every year.
Observers can view the total eclipse on September 27, starting at 10:11 p.m. EDT until 11:23 p.m. This event will be visible in North and South America, as well as Europe and Africa. So make sure to mark your calendars!

This month, you will also be able to see the planets! Look for Mercury, Saturn, Pluto and Neptune in the evening sky. Uranus and Neptune at midnight, and Venus, Mars and Jupiter in the pre-dawn sky.

Finally, if you’re able to escape to a dark location, you might be able to see a great view of our Milky Way!
So, make sure to get outside this month and take a look at everything our night sky has to offer.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 haradrimculture reblogged this · 3 months ago
haradrimculture reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 haradrimculture liked this · 3 months ago
haradrimculture liked this · 3 months ago -
 sleepydreameroncloud9 reblogged this · 3 months ago
sleepydreameroncloud9 reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 annao4str liked this · 7 months ago
annao4str liked this · 7 months ago -
 reallovebb liked this · 9 months ago
reallovebb liked this · 9 months ago -
 almost-correct-quotes liked this · 1 year ago
almost-correct-quotes liked this · 1 year ago -
 lunarssong reblogged this · 1 year ago
lunarssong reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 lunarssong liked this · 1 year ago
lunarssong liked this · 1 year ago -
 fortheloveofscribe reblogged this · 1 year ago
fortheloveofscribe reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 fungiahadiwaff liked this · 1 year ago
fungiahadiwaff liked this · 1 year ago -
 mrneedle liked this · 1 year ago
mrneedle liked this · 1 year ago -
 myth-logic liked this · 1 year ago
myth-logic liked this · 1 year ago -
 studyelephant liked this · 1 year ago
studyelephant liked this · 1 year ago -
 talias-defense-attorney liked this · 2 years ago
talias-defense-attorney liked this · 2 years ago -
 alissa12 liked this · 2 years ago
alissa12 liked this · 2 years ago -
 bloggingmiles liked this · 2 years ago
bloggingmiles liked this · 2 years ago -
 yes-you-are-just-as-sane-as-i-am reblogged this · 2 years ago
yes-you-are-just-as-sane-as-i-am reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 janesurlife liked this · 2 years ago
janesurlife liked this · 2 years ago -
 koachdal reblogged this · 2 years ago
koachdal reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 thecosmickillercat liked this · 2 years ago
thecosmickillercat liked this · 2 years ago
I love space. I've been to space camp in Huntsville Alabama and I am planning on going every summer. I look forward to be an astronaut for nasa on the sls that is planned to be launched 2018. And the manned mission 2030. So yeah I won't let anything get in my way.
138 posts