Your personal Tumblr library awaits
Planetary Rings - Blog Posts
Orange Gem

Picture of the Day - October 28, 2018
Here we have another Titan-Like world with rings. Seas of liquid methane cover the surface, and a thick hazy nitrogen-methane atmosphere obscures most of the surface.
Another Moon Shot

Picture of the day - October 26, 2018
A large moon against the backdrop of a stunningly colorful gas giant and it’s rings.
Double Moons

Picture of the Day - October 17, 2018
A double transit of two moons across the face of a giant ringed planet.

Picture of the Day 2 - October 17,2018
Another wider angle shot
Lunar Shadow

Picture of the Day - October 14, 2018
Small satellite casting its shadow across a gas giant.
Blue Titan

Picture of the day - October 12, 2018.
Blue-tinted Titan-Like world with liquid methane oceans and an extensive ring system.
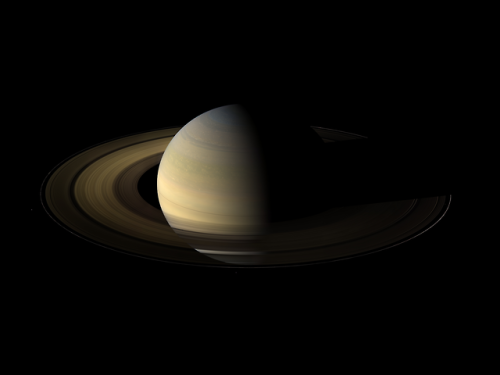
Saturn’s equinox in 2009 taken by Cassini spacecraft
Credit: NASA/JPL






Oculus System - Post 4 (Beautiful Outer Giant)
Here we come across the outer-most planet, a large gas-giant with a violet tint. This giant world has more than 5 times the mass of Jupiter and orbits the sun at an average distance of 7.15 AU. The planet has a beautiful ring system, and is surrounded by a system of 10 spherical satellites.
High Resolution Pics
Picture 1 - Outer-most gas giant - Light Enhanced
Picture 2 - Closeup
Picture 3 - Rising Giant
Picture 4 - Another moon shoot
Picture 5 - Rings over the sly
Picture 6 - Ring Closeup
Ultra-Close Orbits of Saturn = Ultra-Cool Science
On Sept. 15, 2017, our Cassini spacecraft ended its epic exploration of Saturn with a planned dive into the planet’s atmosphere–sending back new science to the very last second. The spacecraft is gone, but the science continues!

New research emerging from the final orbits represents a huge leap forward in our understanding of the Saturn system – especially the mysterious, never-before-explored region between the planet and its rings. Some preconceived ideas are turning out to be wrong while new questions are being raised. How did they form? What holds them in place? What are they made of?

Six teams of researchers are publishing their work Oct. 5 in the journal Science, based on findings from Cassini’s Grand Finale. That’s when, as the spacecraft was running out of fuel, the mission team steered Cassini spectacularly close to Saturn in 22 orbits before deliberately vaporizing it in a final plunge into the atmosphere in September 2017.

Knowing Cassini’s days were numbered, its mission team went for gold. The spacecraft flew where it was never designed to fly. For the first time, it probed Saturn’s magnetized environment, flew through icy, rocky ring particles and sniffed the atmosphere in the 1,200-mile-wide (2,000-kilometer-wide) gap between the rings and the cloud tops. Not only did the engineering push the spacecraft to its limits, the new findings illustrate how powerful and agile the instruments were.
Many more Grand Finale science results are to come, but today’s highlights include:
Complex organic compounds embedded in water nanograins rain down from Saturn’s rings into its upper atmosphere. Scientists saw water and silicates, but they were surprised to see also methane, ammonia, carbon monoxide, nitrogen and carbon dioxide. The composition of organics is different from that found on moon Enceladus – and also different from those on moon Titan, meaning there are at least three distinct reservoirs of organic molecules in the Saturn system.

For the first time, Cassini saw up close how rings interact with the planet and observed inner-ring particles and gases falling directly into the atmosphere. Some particles take on electric charges and spiral along magnetic-field lines, falling into Saturn at higher latitudes – a phenomenon known as “ring rain.” But scientists were surprised to see that others are dragged quickly into Saturn at the equator. And it’s all falling out of the rings faster than scientists thought – as much as 10,000 kg of material per second.

Scientists were surprised to see what the material looks like in the gap between the rings and Saturn’s atmosphere. They knew that the particles throughout the rings ranged from large to small. They thought material in the gap would look the same. But the sampling showed mostly tiny, nanograin- and micron-sized particles, like smoke, telling us that some yet-unknown process is grinding up particles. What could it be? Future research into the final bits of data sent by Cassini may hold the answer.

Saturn and its rings are even more interconnected than scientists thought. Cassini revealed a previously unknown electric current system that connects the rings to the top of Saturn’s atmosphere.

Scientists discovered a new radiation belt around Saturn, close to the planet and composed of energetic particles. They found that while the belt actually intersects with the innermost ring, the ring is so tenuous that it doesn’t block the belt from forming.

Unlike every other planet with a magnetic field in our Solar System, Saturn’s magnetic field is almost completely aligned with its spin axis. Think of the planet and the magnetic field as completely separate things that are both spinning. Both have the same center point, but they each have their own axis about which they spin. But for Saturn the two axes are essentially the same – no other planet does that, and we did not think it was even possible for this to happen. This new data shows a magnetic-field tilt of less than 0.0095 degrees. (Earth’s magnetic field is tilted 11 degrees from its spin axis.) According to everything scientists know about how planetary magnetic fields are generated, Saturn should not have one. It’s a mystery physicists will be working to solve.

Cassini flew above Saturn’s magnetic poles, directly sampling regions where radio emissions are generated. The findings more than doubled the number of reported crossings of radio sources from the planet, one of the few non-terrestrial locations where scientists have been able to study a mechanism believed to operate throughout the universe. How are these signals generated? That’s still a mystery researchers are looking to uncover.
For the Cassini mission, the science rolling out from Grand Finale orbits confirms that the calculated risk of diving into the gap – skimming the upper atmosphere and skirting the edge of the inner rings – was worthwhile.

Almost everything going on in that region turned out to be a surprise, which was the importance of going there, to explore a place we’d never been before. And the expedition really paid off!
Analysis of Cassini data from the spacecraft’s instruments will be ongoing for years to come, helping to paint a clearer picture of Saturn.
To read the papers published in Science, visit: URL to papers
To learn more about the ground-breaking Cassini mission and its 13 years at Saturn, visit: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/cassini/main/index.html
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Image of Saturn taken by the Cassini spacecraft in 2007
Credit: NASA processed by Kevin M. Gill






O’Sirus System - Post 4 (Rings)
Two planets in the O’Sirus System have rings, the 7th and 10th planets respectively.
The 7th planet is an ice-world with a thick icy crust floating on a sub-surface ocean. It is roughly 0.30 Earth-masses, has a radius 75% that of Earth and orbits 1.32 AU from the sun. The surface has a carbon dioxide atmosphere of approximately the same pressure as the atmosphere of Mars and surface temperatures of 133 K or -224 °F.
The 10th world is small ice giant 10.5 times more massive than Earth, has a radius 2.8 times larger than Earth and orbits at a distance of 6.02 AU. This world also has a pronounced ring system.
High Resolution Pics
Picture 1 - The 7th Planet
Picture 2 - Ring Closeup
Picture 3 - Another Closeup
Picture 4 - The 10th Planet
Picture 5 - Closeup
Picture 6- Ring Transit
Ten interesting facts about Saturn
Saturn is sometimes called “The Jewel of the Solar System.” It is a planet that is nothing like our own. Humans have been gazing up at Saturn for a long time. They have been wondering about it for thousands of years.
Here are some fun facts about the Ringed Planet.

Saturn is huge. It is the second largest planet in our Solar System. Jupiter is the only planet that is bigger.

The rings are huge but thin. The main rings could almost go from Earth to the moon. Yet, they are less than a kilometer thick.

Four spacecraft have visited Saturn: Pioneer 11, Voyager 1 and 2, and the Cassini-Huygens mission have all studied the planet.

Saturn has oval-shaped storms similar to Jupiter’s: The region around its north pole has a hexagonal-shaped pattern of clouds. Scientists think this may be a wave pattern in the upper clouds. The planet also has a vortex over its south pole that resembles a hurricane-like storm.

Saturn is made mostly of hydrogen and helium: It exists in layers that get denser farther into the planet. Eventually, deep inside, the hydrogen becomes metallic. At the core lies a hot interior. (click the image for a better resolution).

Saturn has 62 moons: Some of these are large, like Titan, the second largest moon in the Solar System. But most are tiny – just a few km across, and they have no official names. In fact, the last few were discovered by NASA’s Cassini orbiter just a few years ago. More will probably be discovered in the coming years.

Saturn orbits the Sun once every 29.4 Earth years: Its slow movement against the backdrop of stars earned it the nickname of “Lubadsagush” from the ancient Assyrians. The name means “oldest of the old”.

In Saturn there is aurora: Photographic composition made by the Hubble Space Telescope showing the occurrence of aurora in the southern hemisphere of Saturn at intervals of two days.The aurora is visible only in the ultraviolet.

Saturn spins on its axis very fast. A day on Saturn is 10 hours and 14 minutes.

You can see Saturn with your own eyes: Saturn appears as one of the 5 planets visible with the unaided eye. If Saturn is in the sky at night, you can head outside and see it. To see the rings and the ball of the planet itself, you’ll want to peer through a telescope. But you can amaze your friends and family by pointing out that bright star in the sky, and let them know they’re looking at Saturn.
sources: nasa.gov, universetoday.com and solarsystem.nasa.gov