FBI Chief: It’s ‘unacceptable’ That Guardian Has Better Data On Police Violence | See Full Article

FBI chief: It’s ‘unacceptable’ that Guardian has better data on police violence | See full article
The head of the FBI has said it is “ridiculous [and] embarrassing” that the federal government has no better information on police shootings than databases compiled by the Guardian US and the Washington Post.
“It is unacceptable that the Washington Post and the Guardian newspaper from the UK are becoming the lead source of information about violent encounters between [US] police and civilians,” said James Comey, the FBI director.
To see our updated count of police killings in the United States in 2015, visit the Counted database. You can also follow the project on Facebook and Twitter.
Our count as of this afternoon:

More Posts from Dotmpotter and Others



Teen Starts Company To Make Low-Cost Printers To Help Blind People
SANTA CLARA, Calif. (AP) — In Silicon Valley, it’s never too early to become an entrepreneur. Just ask 13-year-old Shubham Banerjee. The California eighth-grader has launched a company to develop low-cost machines to print Braille, the tactile writing system for the visually impaired. Tech giant Intel Corp. recently invested in his startup, Braigo Labs.
For behind this incredible technology go here.

Spatial Agency: Other Ways of Doing Architecture
Nishat Awan
This book offers the first comprehensive overview of alternative approaches to architectural practice. At a time when many commentators are noting that alternative and richer approaches to architectural practice are required if the profession is to flourish, this book provides multiple examples from across the globe of how this has been achieved and how it might be achieved in the future. Particularly pertinent in the current economic climate, this book offers the reader new approaches to architectural practice in a changing world. It makes essential reading for any architect, aspiring or practicing.

From Hawaii’s flurry of hurricanes, to record high sea ice in Antarctica, and a heat wave that cooked the Australian Open like shrimp on a barbie, 2014 saw some wild weather. How much of that was tied to climate change is what scientists around the world tried to answer in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society’s annual attribution report, which was published Thursday.
What they discovered was that the clearest impacts of warming could be found in heat-related events, from heat waves on land to unusually hot ocean waters. Other events, like droughts in East Africa and the Middle East, California’s intense wildfires, and winter storms that continually swept across the eastern U.S., were harder to pinpoint. In part this is because such events are inherently complex, with a multitude of factors influencing them.
For example, while the East African drought was found to be both more likely and more intense because of warming, the situation in the Middle East was less clear, with no discernable climate change connection to the various factors that influenced it. Likewise, no direct push from climate change could be found in California’s wildfire activity, though it is clear that it is increasing the overall wildfire risk there.
And while some events, like the U.S. winter storms and the record high Antarctic sea ice extent, could be pinned to a particular cause, that cause could not be linked to climate change. For other events, like the drought in Brazil and flooding in the Canadian prairies, humans influenced the likelihood in other ways besides the greenhouse gases that continue to be emitted into the atmosphere.
What was clear, though, is that the fast-growing field of what is called extreme event attribution is gaining momentum. Researchers are casting a wider net for extreme events to examine and continually refining their methods. Attribution work has traveled a considerable distance since its inception just over a decade ago.
“Extreme event attribution” is a new topic for me. Very cool science right thar.

Could Europe Be Powered by African Solar Energy?
For a long time, people looking for big fixes to climate change have been talking about building huge solar installations in North Africa, which gets a lot more sun than most of the places where solar power is big — Germany, for example. But now, it looks as if someone finally is doing it.
Next month in Ouarzazate, Morocco, the first portion of what eventually will be the world’s biggest concentrated solar power plant – called Noor I – is set to go online, according to the Guardian, a British newspaper.
Eventually, when the entire $10 billion complex, which is being financed with assistance from the World Bank and European Union, is completed in 2020, it will generate 580 megawatts of electricity, enough to provide a big portion of Morocco’s energy needs while still leaving plenty of juice for export. The complex could prevent 700,000 tons of carbon dioxide from being spewed into the atmosphere each year.
The plant uses an ingenious technology for getting the most out of sunlight. A huge array of 500,000 crescent-shaped mirrors focus sunlight and transmit it to a single point on a tower. (The mirrors actually have tiny computers in them, which adjust the angle throughout the day to gather the most energy.)
The plant could turn Morocco, which depends upon fossil fuel imports to fill 94 percent of its energy needs, into a major producer of electricity for export. Find out how by clicking here.
my man went for it
Governments aren’t doing much to halt global warming but there is hope in the business world. Here are the companies that are facing up to the challenge.
Not my usual climate post. But, BMW is #1.
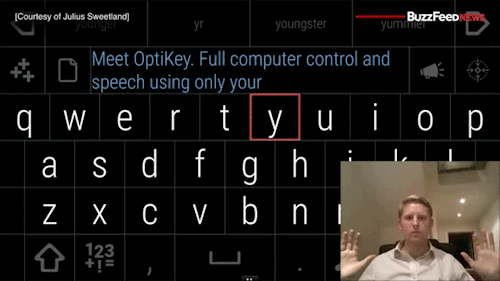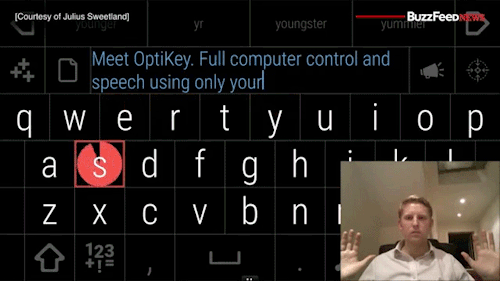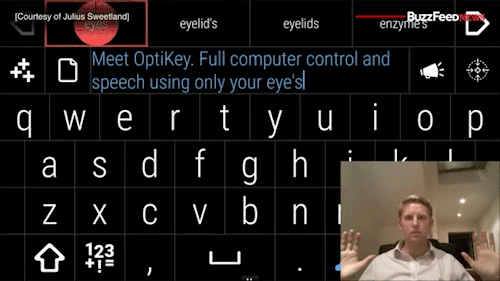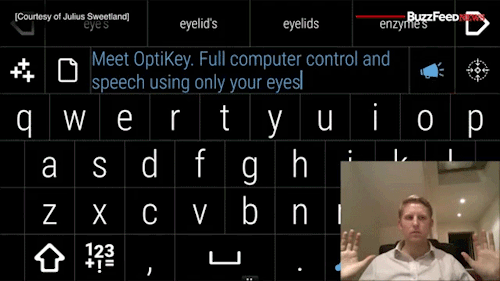





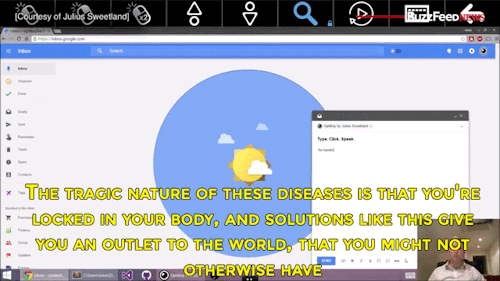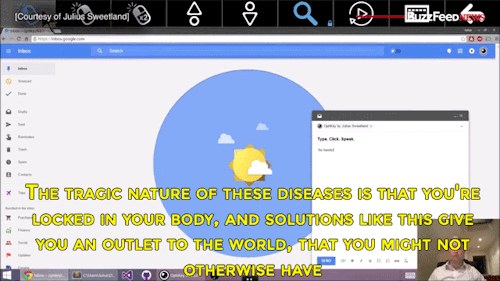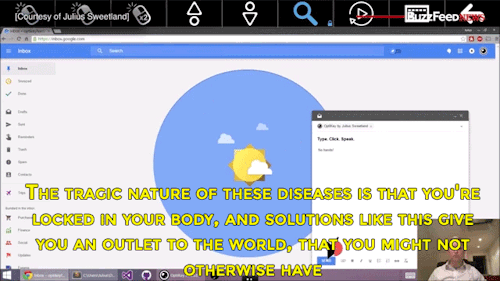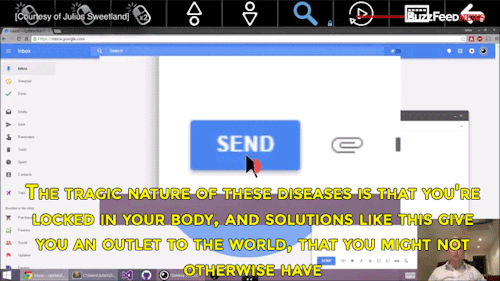

Watch the video of this man giving away his software for free to help people with degenerative diseases communicate

That’s one small hole for a probe, but one giant leap for NASA. This past weekend, the space agency jerry-rigged Curiosity’s malfunctioning drill, allowing the rover to bore into Martian rock for the first time in over a year.
Continue Reading.
Power-pylons that look like looming giants


Choi + Shine, an architecture firm, has proposed modifying Iceland’s existing power-transmission pylons to turn them into looming giants whose arms are poised to reflect their positions – pylons ascending a hill will be posed as though they were scaling its slopes.
The designers claim that it can be made cost-effective through clever engineering, and that the resulting aesthetic experience will be monumental. I agree with the latter statement and am unqualified to assess the former, though Iceland has a weird and cool relationship with power, as it is ia carbon-neutral country whose electricity comes from geothermal sources.
Read the rest
A reliable way to make people believe in falsehoods is frequent repetition, because familiarity is not easily distinguished from truth.
Daniel Kahneman, Thinking, Fast and Slow
-
 mrsdinozzo reblogged this · 8 years ago
mrsdinozzo reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 unbossed reblogged this · 9 years ago
unbossed reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 943bsa liked this · 9 years ago
943bsa liked this · 9 years ago -
 botw2 liked this · 9 years ago
botw2 liked this · 9 years ago -
 darkelf19 reblogged this · 9 years ago
darkelf19 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 kostecko27 liked this · 9 years ago
kostecko27 liked this · 9 years ago -
 getthatbagel reblogged this · 9 years ago
getthatbagel reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 un-decisional reblogged this · 9 years ago
un-decisional reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 cherrypie11 reblogged this · 9 years ago
cherrypie11 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 pterydactylplates reblogged this · 9 years ago
pterydactylplates reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 anindiscriminatecollection reblogged this · 9 years ago
anindiscriminatecollection reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 blackpolosandsweaters reblogged this · 9 years ago
blackpolosandsweaters reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 sugarbutchy reblogged this · 9 years ago
sugarbutchy reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 heisenbair reblogged this · 9 years ago
heisenbair reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 bokemio reblogged this · 9 years ago
bokemio reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 bokemio liked this · 9 years ago
bokemio liked this · 9 years ago -
 dotmpotter reblogged this · 9 years ago
dotmpotter reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 petitlitterateur reblogged this · 9 years ago
petitlitterateur reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 ratedrforviolence reblogged this · 9 years ago
ratedrforviolence reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 ratedrforviolence liked this · 9 years ago
ratedrforviolence liked this · 9 years ago -
 mariahoenenevigglad reblogged this · 9 years ago
mariahoenenevigglad reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 okbae reblogged this · 9 years ago
okbae reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 jenn2d2 reblogged this · 9 years ago
jenn2d2 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 awkwardheart liked this · 9 years ago
awkwardheart liked this · 9 years ago -
 quinoaandbeetroot liked this · 9 years ago
quinoaandbeetroot liked this · 9 years ago -
 mlgpersempre liked this · 9 years ago
mlgpersempre liked this · 9 years ago -
 newideasfor reblogged this · 9 years ago
newideasfor reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 australiancamels reblogged this · 9 years ago
australiancamels reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 roughlyhewn liked this · 9 years ago
roughlyhewn liked this · 9 years ago -
 wsoriacordero liked this · 9 years ago
wsoriacordero liked this · 9 years ago -
 itskavizzile reblogged this · 9 years ago
itskavizzile reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 unknown-regions liked this · 9 years ago
unknown-regions liked this · 9 years ago -
 mx-n-matches reblogged this · 9 years ago
mx-n-matches reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 almostarticulate liked this · 9 years ago
almostarticulate liked this · 9 years ago -
 lunaslashsea reblogged this · 9 years ago
lunaslashsea reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 pinterestmomtbh reblogged this · 9 years ago
pinterestmomtbh reblogged this · 9 years ago
