Your personal Tumblr library awaits
Climate - Blog Posts
the worse climate disaster gets, the more you’ll see closet eugenicists start to advocate for letting people die. you need to be prepared to combat the ideology wherever you see it, because it’s only going to get worse and worse Read everything having to do with climate disaster critically. If the central argument underlying what’s being said is that the death of disabled and/or racialized people is inevitable, natural, or desirable– that’s a fascist.
they might be appear to be a garden variety republican or liberal or even a leftist at first, but know that if that argument is being made, their underlying ideology is one of supremacism, and given additional climate stress, they will become more blatant about it.
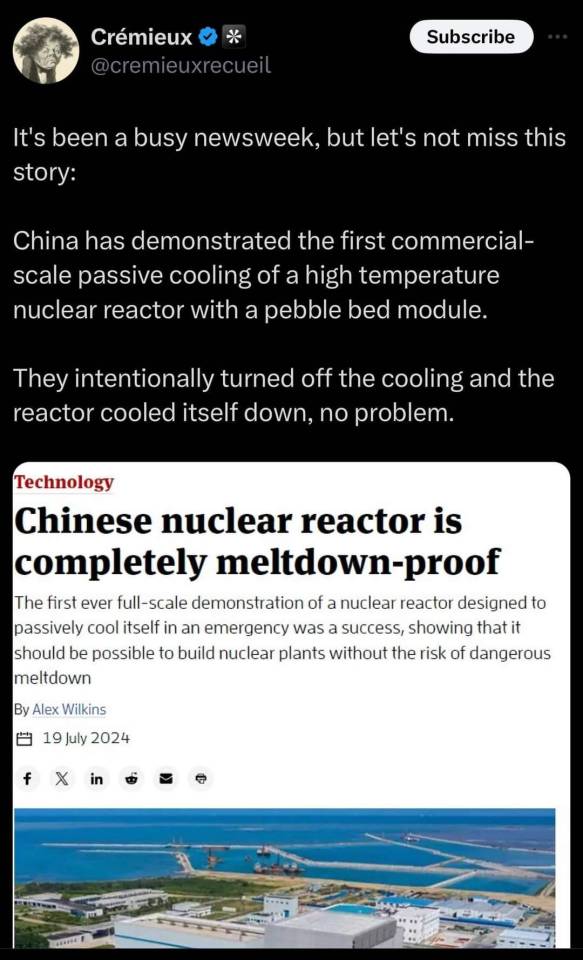
I've recently been seeing this article making rounds around this website and particularly people misusing this very cool advancement to imply that modern nuclear reactors are "unsafe" or "dangerous", which is partially due to the just blatantly bad journalism on display here.
The accomplishment of this new reactor is definitely exceptionally impressive but I think that news websites (Even ones specializing in science) have been mischaracterizing the reactor as "meltdown-proof" which is just - wrong? and implies that current reactors are just begging to meltdown.
The cool thing about this new reactor is that its passively cooled, but that doesn't mean its INVULNERABLE to nuclear meltdowns, for example the Chernobyl meltdown happened completely independently of whether it was cooled passively or not.
In fact, passive cooling would only pose an advantage in situations where ALL pumps and backup pumps break and the core doesn't get coolant pumped to it. That's happened exactly once: in Fukushima and only after a literal tsunami hit it, and there's no reason to think that the passive Helium coolant in this new reactor wouldn't also just break. Fukushima happened because of corruption in regulation, preventing suitable defenses against this exact thing from getting built, not because of unsafe reactor design.
There's also some articles like this one which talk about the new reactor being "self-regulating" which is true, but misses the point that the vast majority of nuclear reactors in service today are also stable in the exact same way. Negative feedback loops are a HUGE part of reactor design, the most popular reactor design today is the Pressurised Water Reactor (PWR) which is incredibly stable - PWRs just truly hate increasing (or decreasing) energy output.
Most nuclear reactors today are already incredibly safe, even if you had complete control over a nuclear reactor it would be effectively impossible to cause a meltdown on purpose - both the physics of the system and the thousands of automated components would beat the ever loving shit out of any hope of trying to do so.
Articles like these just turn this impressive achievements into a kind of fearmongering over the "dangerous" nuclear reactors currently being used. The fact is that nuclear reactors are incredibly safe, PWRs are an incredible feat of engineering genius and its a genuine shame that the general public isn't aware of how much care goes into their design and safety, let alone how useful and essential they are in our electrical systems.
Modern nuclear reactors are clean, they are safe, and they are vital to a healthy energy grid in the post-fossil-fuel future.
A really good read I highly recommend is Colin Tucker's How To Drive A Nuclear Reactor. He's very clear and very frank with the workings and reality of nuclear power today.




Sean bienvenidos japonistasarqueologicos a una nueva entrega del país del sol naciente en la que os explicaré que es el tsuyu, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos que empezamos. - ¿Qué es el tsuyu? ¿En qué consiste? El tsuyu, en hiragana つゆ y en kanji corresponde a 梅雨. Esto corresponde a los meses de verano en Japón: Mayo a julio seguramente todos habréis visto la película de Tenki no ko, del director Makoto shinkai, en el que se puede apreciar muy bien este fenómeno por poner un ejemplo. En estos dos meses caen grandes trombas de agua a raudales que para algunos le resultará placentero y otros una tortura¿Qué es para vosotros?, ¿os gustan los periodos de lluvia? - Espero que os haya gustado y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones que pasen una linda semana. - 日本の考古学者諸君、ようこそ、日出ずる国の新連載へ。ツユとは何かを説明しよう。 - ツユとは何か?つゆとは、ひらがなでは「つゆ」、漢字では「梅雨」にあたる。皆さんは新海誠監督の映画『天 気の子』をご覧になったことがあるだろう。この2ヶ月間、滔々と降り注ぐ大雨は、ある人にとっては喜びであり、ある人にとっては拷問である。 あなたは雨の時期が好きですか? - それでは、また次の記事でお会いしましょう。 - Welcome, Japanese archaeologists, to a new installment of the land of the rising sun in which I will explain to you what the tsuyu is, having said that, make yourselves comfortable and let's get started. - What is tsuyu and what does it consist of? Tsuyu, in hiragana つゆ and in kanji it would correspond to 梅雨. This corresponds to the summer months in Japan: May to July, you have probably all seen the film Tenki no ko, by director Makoto Shinkai, in which this phenomenon can be seen very well, to give an example. In these two months, huge downpours of water fall in torrents, which for some people will be a pleasure and for others a torture. What is it like for you, do you like periods of rain? - I hope you liked it and see you in the next posts have a nice week.
Y'all I know that when so-called AI generates ridiculous results it's hilarious and I find it as funny as the next guy but I NEED y'all to remember that every single time an AI answer is generated it uses 5x as much energy as a conventional websearch and burns through 10 ml of water. FOR EVERY ANSWER. Each big llm is equal to 300,000 kiligrams of carbon dioxide emissions.
LLMs are killing the environment, and when we generate answers for the lolz we're still contributing to it.
Stop using it. Stop using it for a.n.y.t.h.i.n.g. We need to kill it.
Sources:




Sharpening Our View of Climate Change with the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem Satellite
As our planet warms, Earth’s ocean and atmosphere are changing.
Climate change has a lot of impact on the ocean, from sea level rise to marine heat waves to a loss of biodiversity. Meanwhile, greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide continue to warm our atmosphere.
NASA’s upcoming satellite, PACE, is soon to be on the case!
Set to launch on Feb. 6, 2024, the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission will help us better understand the complex systems driving the global changes that come with a warming climate.

Earth’s ocean is becoming greener due to climate change. PACE will see the ocean in more hues than ever before.
While a single phytoplankton typically can’t be seen with the naked eye, communities of trillions of phytoplankton, called blooms, can be seen from space. Blooms often take on a greenish tinge due to the pigments that phytoplankton (similar to plants on land) use to make energy through photosynthesis.
In a 2023 study, scientists found that portions of the ocean had turned greener because there were more chlorophyll-carrying phytoplankton. PACE has a hyperspectral sensor, the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), that will be able to discern subtle shifts in hue. This will allow scientists to monitor changes in phytoplankton communities and ocean health overall due to climate change.

Phytoplankton play a key role in helping the ocean absorb carbon from the atmosphere. PACE will identify different phytoplankton species from space.
With PACE, scientists will be able to tell what phytoplankton communities are present – from space! Before, this could only be done by analyzing a sample of seawater.
Telling “who’s who” in a phytoplankton bloom is key because different phytoplankton play vastly different roles in aquatic ecosystems. They can fuel the food chain and draw down carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to photosynthesize. Some phytoplankton populations capture carbon as they die and sink to the deep ocean; others release the gas back into the atmosphere as they decay near the surface.
Studying these teeny tiny critters from space will help scientists learn how and where phytoplankton are affected by climate change, and how changes in these communities may affect other creatures and ocean ecosystems.

Climate models are one of our most powerful tools to understand how Earth is changing. PACE data will improve the data these models rely on.
The PACE mission will offer important insights on airborne particles of sea salt, smoke, human-made pollutants, and dust – collectively called aerosols – by observing how they interact with light.
With two instruments called polarimeters, SPEXone and HARP2, PACE will allow scientists to measure the size, composition, and abundance of these microscopic particles in our atmosphere. This information is crucial to figuring out how climate and air quality are changing.
PACE data will help scientists answer key climate questions, like how aerosols affect cloud formation or how ice clouds and liquid clouds differ.
It will also enable scientists to examine one of the trickiest components of climate change to model: how clouds and aerosols interact. Once PACE is operational, scientists can replace the estimates currently used to fill data gaps in climate models with measurements from the new satellite.

With a view of the whole planet every two days, PACE will track both microscopic organisms in the ocean and microscopic particles in the atmosphere. PACE’s unique view will help us learn more about the ways climate change is impacting our planet’s ocean and atmosphere.
Stay up to date on the NASA PACE blog, and make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of sPACE!

Six Answers to Questions You’re Too Embarrassed to Ask about the Hottest Year on Record
You may have seen the news that 2023 was the hottest year in NASA’s record, continuing a trend of warming global temperatures. But have you ever wondered what in the world that actually means and how we know?
We talked to some of our climate scientists to get clarity on what a temperature record is, what happened in 2023, and what we can expect to happen in the future… so you don’t have to!

1. Why was 2023 the warmest year on record?
The short answer: Human activities. The release of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere trap more heat near Earth’s surface, raising global temperatures. This is responsible for the decades-long warming trend we’re living through.
But this year’s record wasn’t just because of human activities. The last few years, we’ve been experiencing the cooler phase of a natural pattern of Pacific Ocean temperatures called the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO). This phase, known as La Niña, tends to cool temperatures slightly around the world. In mid-2023, we started to shift into the warmer phase, known as El Niño. The shift ENSO brought, combined with overall human-driven warming and other factors we’re continuing to study, pushed 2023 to a new record high temperature.

2. So will every year be a record now?
Almost certainly not. Although the overall trend in annual temperatures is warmer, there’s some year-to-year variation, like ENSO we mentioned above.
Think about Texas and Minnesota. On the whole, Texas is warmer than Minnesota. But some days, stormy weather could bring cooler temperatures to Texas while Minnesota is suffering through a local heat wave. On those days, the weather in Minnesota could be warmer than the weather in Texas. That doesn’t mean Minnesota is warmer than Texas overall; we’re just experiencing a little short-term variation.
Something similar happens with global annual temperatures. The globe will naturally shift back to La Niña in the next few years, bringing a slight cooling effect. Because of human carbon emissions, current La Niña years will be warmer than La Niña years were in the past, but they’ll likely still be cooler than current El Niño years.

3. What do we mean by “on record”?
Technically, NASA’s global temperature record starts in 1880. NASA didn’t exist back then, but temperature data were being collected by sailing ships, weather stations, and scientists in enough places around the world to reconstruct a global average temperature. We use those data and our modern techniques to calculate the average.
We start in 1880, because that’s when thermometers and other instruments became technologically advanced and widespread enough to reliably measure and calculate a global average. Today, we make those calculations based on millions of measurements taken from weather stations and Antarctic research stations on land, and ships and ocean buoys at sea. So, we can confidently say 2023 is the warmest year in the last century and a half.

However, we actually have a really good idea of what global climate looked like for tens of thousands of years before 1880, relying on other, indirect ways of measuring temperature. We can look at tree rings or cores drilled from ice sheets to reconstruct Earth’s more ancient climate. These measurements affirm that current warming on Earth is happening at an unprecedented speed.
4. Why does a space agency keep a record of Earth’s temperature?
It’s literally our job! When NASA was formed in 1958, our original charter called for “the expansion of human knowledge of phenomena in the atmosphere and space.” Our very first space missions uncovered surprises about Earth, and we’ve been using the vantage point of space to study our home planet ever since. Right now, we have a fleet of more than 20 spacecraft monitoring Earth and its systems.
Why we created our specific surface temperature record – known as GISTEMP – actually starts about 25 million miles away on the planet Venus. In the 1960s and 70s, researchers discovered that a thick atmosphere of clouds and carbon dioxide was responsible for Venus’ scorchingly hot temperatures.

Dr. James Hansen was a scientist at the Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York, studying Venus. He realized that the greenhouse effect cooking Venus’ surface could happen on Earth, too, especially as human activities were pumping carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
He started creating computer models to see what would happen to Earth’s climate as more carbon dioxide entered the atmosphere. As he did, he needed a way to check his models – a record of temperatures at Earth’s surface over time, to see if the planet was indeed warming along with increased atmospheric carbon. It was, and is, and NASA’s temperature record was born.
5. If last year was record hot, why wasn’t it very hot where I live?
The temperature record is a global average, so not everywhere on Earth experienced record heat. Local differences in weather patterns can influence individual locations to be hotter or colder than the globe overall, but when we average it out, 2023 was the hottest year.
Just because you didn’t feel record heat this year, doesn’t mean you didn’t experience the effects of a warming climate. 2023 saw a busy Atlantic hurricane season, low Arctic sea ice, raging wildfires in Canada, heat waves in the U.S. and Australia, and more.

And these effects don’t stay in one place. For example, unusually hot and intense fires in Canada sent smoke swirling across the entire North American continent, triggering some of the worst air quality in decades in many American cities. Melting ice at Earth’s poles drives rising sea levels on coasts thousands of miles away.

6. Speaking of which, why is the Arctic – one of the coldest places on Earth – red on this temperature map?
Our global temperature record doesn’t actually track absolute temperatures. Instead, we track temperature anomalies, which are basically just deviations from the norm. Our baseline is an average of the temperatures from 1951-1980, and we compare how much Earth’s temperature has changed since then.
Why focus on anomalies, rather than absolutes? Let’s say you want to track if apples these days are generally larger, smaller, or the same size as they were 20 years ago. In other words, you want to track the change over time.
Apples grown in Florida are generally larger than apples grown in Alaska. Like, in real life, how Floridian temperatures are generally much higher than Alaskan temperatures. So how do you track the change in apple sizes from apples grown all over the world while still accounting for their different baseline weights?
By focusing on the difference within each area rather than the absolute weights. So in our map, the Arctic isn’t red because it’s hotter than Bermuda. It’s red because it’s gotten relatively much warmer than Bermuda has in the same time frame.
Want to learn more about climate change? Dig into the data at climate.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
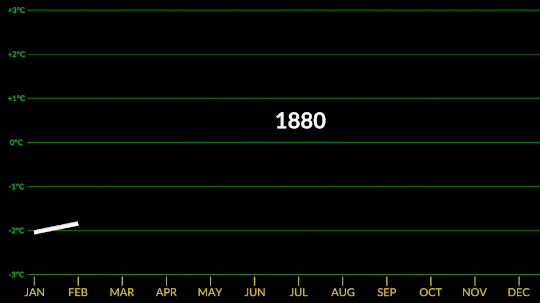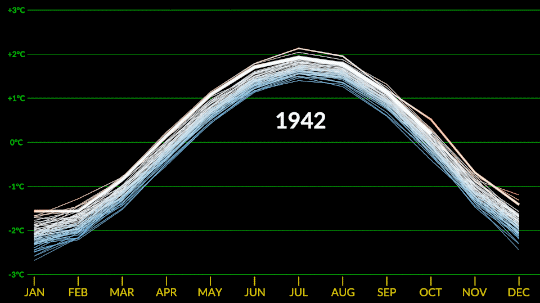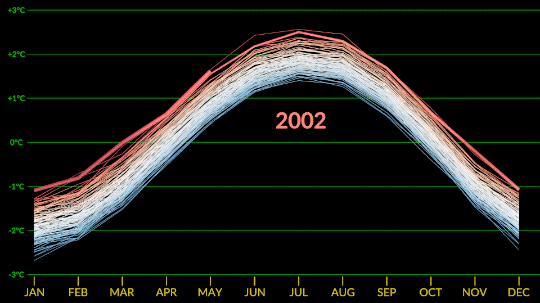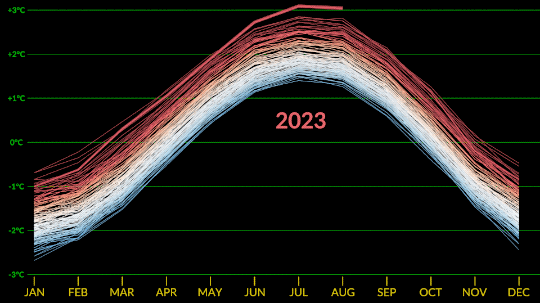
Confirmed: Summer 2023 Hottest in NASA’s Record
All three months of summer 2023 broke records. July 2023 was the hottest month ever recorded, and the hottest July. June 2023 was the hottest June, and August 2023 was the hottest August.
NASA’s temperature record, GISTEMP, starts in 1880, when consistent, modern recordkeeping became possible. Our record uses millions of measurements of surface temperature from weather stations, ships and ocean buoys, and Antarctic research stations. Other agencies and organizations who keep similar global temperature records find the same pattern of long-term warming.
Global temperatures are rising from increased emissions of greenhouse gasses, like carbon dioxide and methane. Over the last 200 years, humans have raised atmospheric CO2 by nearly 50%, primarily through the burning of fossil fuels.
Drivers of climate change, both natural and human-caused, leave distinct fingerprints. Through observations and modeling, NASA researchers confirm that the current warming is the result of human activities, particularly increased greenhouse gas emissions.
Celebrate Earth Day with NASA

"We came all this way to explore the Moon, and the most important thing is that we discovered the Earth." - Apollo 8 astronaut Bill Anders
On Dec. 24, 1968, Anders snapped this iconic photo of "Earthrise" during the historic Apollo 8 mission. As he and fellow astronauts Frank Borman and Jim Lovell became the first humans to orbit the Moon, they witnessed Earth rising over the Moon's horizon. The image helped spark the first #EarthDay on April 22, 1970.
Anders sat down with Dr. Kate Calvin, our chief scientist and senior climate advisor, to chat about the photo, and NASA’s role in studying our home.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Why Isn’t Every Year the Warmest Year on Record?
This just in: 2022 effectively tied for the fifth warmest year since 1880, when our record starts. Here at NASA, we work with our partners at NOAA to track temperatures across Earth’s entire surface, to keep a global record of how our planet is changing.
Overall, Earth is getting hotter.

The warming comes directly from human activities – specifically, the release of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels. We started burning fossil fuels in earnest during the Industrial Revolution. Activities like driving cars and operating factories continue to release greenhouse gases into our atmosphere, where they trap heat in the atmosphere.

So…if we’re causing Earth to warm, why isn’t every year the hottest year on record?
As 2022 shows, the current global warming isn’t uniform. Every single year isn’t necessarily warmer than every previous year, but it is generally warmer than most of the preceding years. There’s a warming trend.
Earth is a really complex system, with various climate patterns, solar activity, and events like volcanic eruptions that can tip things slightly warmer or cooler.
Climate Patterns
While 2021 and 2022 continued a global trend of warming, they were both a little cooler than 2020, largely because of a natural phenomenon known as La Niña.
La Niña is one third of a climate phenomenon called El Niño Southern Oscillation, also known as ENSO, which can have significant effects around the globe. During La Niña years, ocean temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean cool off slightly. La Niña’s twin, El Niño brings warmer temperatures to the central and eastern Pacific. Neutral years bring ocean temperatures in the region closer to the average.

El Niño and La Niña affect more than ocean temperatures – they can bring changes to rainfall patterns, hurricane frequency, and global average temperature.
We’ve been in a La Niña mode the last three, which has slightly cooled global temperatures. That’s one big reason 2021 and 2022 were cooler than 2020 – which was an El Niño year.
Overall warming is still happening. Current El Niño years are warmer than previous El Niño years, and the same goes for La Niña years. In fact, enough overall warming has occurred that most current La Niña years are warmer than most previous El Niño years. This year was the warmest La Niña year on record.

Solar Activity
Our Sun cycles through periods of more and less activity, on a schedule of about every 11 years. Here on Earth, we might receive slightly less energy — heat — from the Sun during quieter periods and slightly more during active periods.

At NASA, we work with NOAA to track the solar cycle. We kicked off a new one – Solar Cycle 25 – after solar minimum in December 2019. Since then, solar activity has been slightly ramping up.
Because we closely track solar activity, we know that over the past several decades, solar activity hasn't been on the rise, while greenhouse gases have. More importantly, the "fingerprints" we see on the climate, including temperature changes in the upper atmosphere, don't fit the what we'd expect from solar-caused warming. Rather they look like what we expect from increased greenhouse warming, verifying a prediction made decades ago by NASA.
Volcanic Eruptions
Throughout history, volcanoes have driven major shifts in Earth’s climate. Large eruptions can release water vapor — a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide — which traps additional warmth within our atmosphere.
On the flip side, eruptions that loft lots of ash and soot into the atmosphere can temporarily cool the climate slightly, by reflecting some sunlight back into space.
Like solar activity, we can monitor volcanic eruptions and tease out their effect on variations in our global temperature.

At the End of the Day, It’s Us
Our satellites, airborne missions, and measurements from the ground give us a comprehensive picture of what’s happening on Earth every day. We also have computer models that can skillfully recreate Earth’s climate.
By combining the two, we can see what would happen to global temperature if all the changes were caused by natural forces, like volcanic eruptions or ENSO. By looking at the fingerprints each of these climate drivers leave in our models, it’s perfectly clear: The current global warming we’re experiencing is caused by humans.
For more information about climate change, visit climate.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
5 Ways Studying Water Will Help Us Better Understand Earth
Studying our home planet is just as powerful as exploring what’s beyond it.
Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) is a joint mission developed by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. It will track water on more than 90% of Earth’s surface and help communities, scientists, and researchers better understand this finite and vital resource. And it’s launching this month!
So how will SWOT help us better understand Earth? Here are 5 ways.

SWOT will address some of the most pressing climate change questions of our time.
An important part of predicting our future climate is determining at what point Earth’s ocean water slows down its absorption of the excess heat in the atmosphere and starts releasing that heat back into the air, where it could accelerate global warming. SWOT will provide crucial information about this global heat exchange between the ocean and the atmosphere, enabling researchers to test and improve future climate forecasts.
The satellite will also offer insights to improve computer models for sea level rise projections and coastal flood forecasting.
Data from SWOT will additionally help scientists, engineers, water managers, and others better monitor drought conditions in lakes and reservoirs and improve flood forecasts for rivers.

SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on the planet’s surface.
SWOT will measure the height of water in Earth’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean, giving scientists the ability to track the movement of water around the world.
SWOT’s eye in the sky will provide a truly global view of the water on more than 90% of Earth’s surface, enriching humankind’s understanding of how the ocean reacts to and influences climate change along with what potential hazards – including floods – lie ahead in different regions of the world.

SWOT will see Earth’s water in higher definition than ever before.
Because everything is better in HD 😉, SWOT will view Earth’s ocean and freshwater bodies with unprecedented clarity compared to other satellites, much like a high-definition television delivers a picture far more detailed than older models. This means that SWOT will be able to “see” ocean features – like fronts and eddies – that are too small for current space-based instruments to detect. Those measurements will help improve researchers’ understanding of the ocean’s role in climate change.
Not only will the satellite show where – and how fast – sea level is rising, it will also reveal how coastlines around the world are changing. It will provide similar high-definition clarity for Earth’s lakes, rivers, and reservoirs, many of which remain a mystery to researchers, who aren’t able to outfit every water body with monitoring instruments.

SWOT data will be used to help make decisions about our daily lives and livelihoods.
As climate change accelerates the water cycle, more communities around the world will be inundated with water while others won’t have enough. SWOT data will be used to monitor drought conditions and improve flood forecasts, providing essential information to water management agencies, disaster preparedness agencies, universities, civil engineers, and others who need to track water in their local areas. SWOT data also will help industries, like shipping, by providing measurements of water levels along rivers, as well as ocean conditions, including tides, currents, and storm surges.

Finally … SWOT will pave the way for future Earth missions.
With its innovative technology and commitment to engaging a diverse community of people who plan to use data from the mission, SWOT is blazing a trail for future Earth-observing missions. SWOT’s data and the tools to support researchers in analyzing the information will be free and accessible. This will help to foster research and applications activities by a wide range of users, including scientists, resource managers, and others who in the past may not have had the opportunity to access this kind of information. Lessons learned from SWOT will lead to new questions and improvements for future missions, including our upcoming Earth System Observatory, a constellation of missions focused on studying key aspects of our home planet.

Keep track of the mission here. And make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
How Climate Change Showed Up in 2021
2021 was tied for the sixth-hottest year since modern record keeping began. We work together with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration to track temperatures around the world and study how they change from year to year.

For decades, the overall global temperature has been increasing because of human activities. The last decade has been the warmest on record. Each individual year’s average temperature, however, can be affected by things like ocean circulation, volcanic eruptions, and specific weather events.
For instance, last year we saw the beginning of La Niña – a pattern of cooler waters in the Pacific – that was responsible for slightly cooling 2021’s average temperature. Still, last year continued a long-term trend of global warming.
Globally, Earth’s temperature in 2021 was nearly 2°F warmer than the late 19th Century, for the seventh year in a row.

The Record
Studying 142 Years
Since 1880, we can put together a consistent record of temperatures around the planet and see that it was much colder in the late-19th century. Before 1880, uncertainties in tracking global temperatures are larger. Temperatures have increased even faster since the 1970s, the result of increasing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Tracking Millions of Individual Observations
Our scientists use millions of individual observations of data from more than 20,000 weather stations and Antarctic research stations, together with ship- and buoy-based observations of sea surface temperatures, to track global temperatures.

Reviewing Multiple Independent Records
Our global temperature record – GISTEMP – is one of a number of independent global temperature records, all of which show the same pattern of warming.

The Consequences
Everywhere Experiences Climate Change Differently
As Earth warms, temperature changes occur unevenly around the globe. The Arctic is currently warming about four times faster than the rest of the planet – a process called Arctic amplification. Similarly, urban areas tend to warm faster than rural areas, partly because building materials like asphalt, steel and concrete retain heat.

Droughts and Floods in Warmer Weather
More than 88% of the Western US experienced drought conditions in 2021. At the same time, communities in Western Europe saw two months’ worth of rain in 24 hours, breaking records and triggering flash floods. Because a hotter climate means more water can be carried in the atmosphere, areas like the Western US suffer drought from the increased 'thirstiness' of the atmosphere, while precipitation events can become more extreme as the amount of moisture in the atmosphere rises.

Sea Levels Continue to Rise
Melting ice raises sea levels around the world, as meltwater drains into the ocean. In addition, heat causes the ocean water to expand. From 1993 to today, global mean sea level has been rising around 3.4 millimeters per year. In 2021, sea level data from the recently launched NASA/ESA Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission became available to the public.

There is Hope
“This is not good news, but the fact that we are able to track this in real time and understand why it’s changing, and get people to notice why it’s changing and how we can change things to change the next trajectory, that gives me hope. Because we’re not in the dark here. We’re not the dinosaurs who are unaware the comet is coming. We can see the comet coming, and we can act.” – Dr. Gavin Schmidt, director of NASA GISS, where the global temperature record is calculated
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
NASA Sees Our Ocean in Color. How About You?
Take a deep breath. Feel the oxygen in your lungs. We have the ocean to thank for that! Over long time scales, between 50 and 70 percent of our planet's oxygen is produced by microscopic organisms living in the ocean.

Today is World Oceans Day! And as our planet’s climate continues to change, we want to understand how one of our biggest ecosystems is changing with it. Wondering how you can celebrate with NASA? We’ve got downloadable coloring pages and online coloring interactives to show how we study the ocean. Read on.
From Space to Sea

Download ocean missions coloring page here Download Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich coloring page here
We use planes, boats, Earth-observing satellites and much more to study the ocean and partner with organizations all over the world. Here are a few examples:
From Sea
The Export Processes in the Ocean from Remote Sensing (EXPORTS) is one way we study the ocean from the sea to study changes in the ocean’s carbon cycle. In May, scientists and crew conducted research on three ships in the Northern Atlantic Ocean. They hope to create models to better understand climate change patterns.
From Space
Launched last year, the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft began a five-and-a-half-year prime mission to collect the most accurate data yet on global sea level and how our oceans are rising in response to climate change. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is just one of many satellites monitoring the ocean from space. Together with other Earth-observing spacecraft, the mission will also collect precise data of atmospheric temperature and humidity to help improve weather forecasts and climate models.
Finding Eddies

Download Eddies Coloring Page The ocean is full of eddies – swirling water masses that look like hurricanes in the atmosphere. Eddies are often hot spots for biological activity that plays an important role in absorbing carbon. . We find eddies by looking for small changes in the height of the ocean surface, using multiple satellites continuously orbiting Earth. We also look at eddies up close, using ships and planes to study their role in the carbon cycle.
Monitoring Aerosols and Clouds

Clouds coloring interactive here
Aerosols coloring interactive here
Tiny particles in the air called aerosols interact with clouds. These interactions are some of the most poorly understood components of Earth's climate system. Clouds and aerosols can absorb, scatter or reflect incoming radiation -- heat and light from the Sun -- depending on their type, abundance and locations in the atmosphere. We’re building new instruments to better understand aerosols and contribute to air quality forecasts.
The Ocean in Living Color Download PACE coloring page here

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission will continue and greatly advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as Earth’s carbon cycle and atmospheric aerosols and clouds. It’s set to launch in late 2023 to early 2024. Want to learn more? Click here to see how PACE will collect data and here to see what PACE will see through our coloring interactives. (Make sure to check out the hidden surprises in both!)
Exploring Ocean Worlds on Earth and Beyond
Download Clouds coloring page here

Using our understanding of oceans on Earth, we also study oceans on other planets. Mars, for example, contains water frozen in the ice caps or trapped beneath the soil. But there’s even more water out there. Planets and moons in our solar system and beyond have giant oceans on their surface. Saturn’s moon Enceladus is thought to have a massive ocean under its frozen surface, which sometimes sprays into space through massive fissures in the ice.
Learn more about ocean worlds here: nasa.gov/oceanworlds
Interested in learning more about how NASA studies oceans? Follow @NASAClimate, @NASAOcean and @NASAEarth.
You can also find all the coloring pages and interactives here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
In a Warming World, NASA’s Eyes Offer Crucial Views of Hurricanes
June 1 marks the start of hurricane season in the Atlantic Ocean. Last year’s hurricane season saw a record-setting 30 named storms. Twelve made landfall in the United States, also a record. From space, NASA has unique views of hurricanes and works with other government agencies -- like the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) -- to better understand individual storms and entire hurricane seasons.

Here, five ways NASA is changing hurricane science:
1. We can see storms from space
From space, we can see so much more than what’s visible to the naked eye. Among our missions, NASA and NOAA have joint satellite missions monitoring storms in natural color -- basically, what our eyes see -- as well as in other wavelengths of light, which can help identify features our eyes can’t on their own. For instance, images taken in infrared can show the temperatures of clouds, as well as allow us to track the movement of storms at night.

2. We can see inside hurricanes in 3D
If you’ve ever had a CT scan or X-ray done, you know how important 3D imagery can be to understanding what’s happening on the inside. The same concept applies to hurricanes. Our Global Precipitation Measurement mission’s radar and microwave instruments can see through storm clouds to see the precipitation structure of the storm and measure how much total rain is falling as a result of the storm. This information helps scientists understand how the storm may change over time and understand the risk of severe flooding.
We can even virtually fly through hurricanes!

3. We’re looking at how climate change affects hurricane behavior
Climate change is likely causing storms to behave differently. One change is in how storms intensify: More storms are increasing in strength quickly, a process called rapid intensification, where hurricane wind speeds increase by 35 mph (or more) in just 24 hours.
In 2020, a record-tying nine storms rapidly intensified. These quick changes in storm strength can leave communities in their path without time to properly prepare.
Researchers developed a machine learning model that could more accurately detect rapidly intensifying storms.

It’s not just about how quickly hurricanes gain strength. We’re also looking at how climate change may be causing storms to move more slowly, which makes them more destructive. These “stalled” storms can slow to just a few miles an hour, dumping rain and damaging winds on one location at a time. Hurricane Dorian, for example, stalled over Grand Bahama and left catastrophic damage in its wake. Hurricanes Harvey and Florence experienced stalling as well, both causing major flooding.

4. We can monitor damage done by hurricanes
Hurricane Maria reshaped Puerto Rico’s forests. The storm destroyed so many large trees that the overall height of the island’s forests was shortened by one-third. Measurements from the ground, the air, and space gave researchers insights into which trees were more susceptible to wind damage.

Months after Hurricane Maria, parts of Puerto Rico still didn’t have power. Using satellite data, researchers mapped which neighborhoods were still dark and analyzed demographics and physical attributes of the areas with the longest wait for power.

5. We help communities prepare for storms and respond to their aftermath
The data we collect is available for free to the public. We also partner with other federal agencies, like the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), and regional and local governments to help prepare for and understand the impacts of disasters like hurricanes.
In 2020, our Disasters Program provided data to groups in Alabama, Louisiana, and Central America to identify regions significantly affected by hurricanes. This helps identify vulnerable communities and make informed decisions about where to send resources.

The 2021 Atlantic hurricane season starts today, June 1. Our colleagues at NOAA are predicting another active season, with an above average number of named storms. At NASA, we’re developing new technology to study how storms form and behave, including ways to understand Earth as a system. Working together with our partners at NOAA, FEMA and elsewhere, we’re ready to help communities weather another year of storms.
Bonus: We see storms on other planets, too!
Earth isn’t the only planet with storms. From dust storms on Mars to rains made of glass, we study storms and severe weather on planets in our solar system and beyond. Even the Sun has storms. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot, for instance, is a hurricane-like storm larger than the entire Earth.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

NASA Spotlight: Earth Climate Scientist Dr. Yolanda Shea
Dr. Yolanda Shea is a climate scientist at NASA's Langley Research Center. She’s the project scientist for the CLARREO Pathfinder (CPF) mission, which is an instrument that will launch to the International Space Station to measure sunlight reflected from Earth. It will help us understand how much heat is being trapped by our planet’s atmosphere. Her mission is designed to help us get a clearer picture than we currently have of the Earth’s system and how it is changing
Yolanda took time from studying our home planet to answer questions about her life and career! Get to know this Earth scientist:
What inspired you to study climate science?
Starting in early middle school I became interested in the explanations behind the weather maps and satellite images shown on TV. I liked how the meteorologists talked about the temperature, moisture, and winds at different heights in the atmosphere, and then put that together to form the story of our weather forecasts. This made me want to learn more about Earth science, so I went to college to explore this interest more.
The summer after my junior year of college, I had an internship during which my first assignment was to work with a program that estimated ocean currents from satellite measurements. I was fascinated in the fact that scientists had discovered a way to map ocean currents from space!
Although I had learned about Earth remote sensing in my classes, this was my first taste of working with, and understanding the details of, how we could learn more about different aspects of the physical world from satellite measurements.
This led to my learning about other ways we can learn about Earth from space, and that includes rigorous climate monitoring, which is the area I work in now.

What does a day in your life look like?
Before I start my workday, I like to take a few minutes to eat breakfast, knit (I’m loving sock knitting right now!), and listen to a podcast or audio book. Each workday really looks different for me, but regardless, most days are a combination of quieter moments that I can use for individual work and more interactive times when I’m interfacing with colleagues and talking about project or science issues. Both types of work are fun in different ways, but I’m glad I have a mixture because all researchers need that combination of deep thinking to wrap our minds around complex problems and also time to tackle those problems with others and work on solving them together.
When do you feel most connected to Earth?
I’ve always loved sunsets. I find them peaceful and beautiful, and I love how each one is unique. They are also a beautiful reminder of the versatility of reflected light, which I study. Sitting for a moment to appreciate the beauty and calm I feel during a sunset helps me feel connected to Earth.

What will your mission – CLARREO Pathfinder – tell us about Earth?
CLARREO Pathfinder (CPF) includes an instrument that will take measurements from the International Space Station and will measure reflected sunlight from Earth. One of its goals is to demonstrate that it can take measurements with high enough accuracy so that, if we have such measurements over long periods of time, like several decades, we could detect changes in Earth’s climate system. The CPF instrument will do this with higher accuracy than previous satellite instruments we’ve designed, and these measurements can be used to improve the accuracy of other satellite instruments.
How, if at all, has your worldview changed as a result of your work in climate science?
The longer I work in climate science and learn from the data about how humans have impacted our planet, the more I appreciate the fragility of our one and only home, and the more I want to take care of it.

What advice would you give your younger self?
It’s ok to not have everything figured out at every step of your career journey. Work hard, do your best, and enjoy the journey as it unfolds. You’ll inevitably have some surprises along the way, and regardless of whether they are welcome or not, you’re guaranteed to learn something.
Do you have a favorite metaphor or analogy that you use to describe what you do, and its impact, to those outside of the scientific community?
I see jigsaw puzzles as a good illustration of how different members of a science community play a diverse set of roles to work through different problems. Each member is often working on their own image within the greater puzzle, and although it might take them years of work to see their part of the picture come together, each image in the greater puzzle is essential to completing the whole thing. During my career, I’ll work on a section of the puzzle, and I hope to connect my section to others nearby, but we may not finish the whole puzzle. That’s ok, however, because we’ll hand over the work that we’ve accomplished to the next generation of scientists, and they will keep working to bring the picture to light. This is how I try to think about my role in climate science – I hope to contribute to the field in some way; the best thing about what I have done and what I will do, is that someone else will be able to build on my work and keep helping humanity come to a better understanding of our Earth system.
What is a course that you think should be part of required school curriculum?
Time and project management skills – I think students tend to learn these skills more organically from their parents and teachers, but in my experience I stumbled along and learned these skills through trial and error. To successfully balance all the different projects that I support now, I have to be organized and disciplined, and I need to have clear plans mapped out, so I have some idea of what’s coming and where my attention needs to be focused.
Another course not specifically related to my field is personal financial management. I was interested in personal finance, and that helped me to seek out information (mainly through various blogs) about how to be responsible with my home finances. There is a lot of information out there, but making sure that students have a solid foundation and know what questions to ask early on will set them to for success (and hopefully fewer mistakes) later on.

What’s the most unexpected time or place that your expertise in climate science and/or algorithms came in handy?
I think an interesting part of being an atmospheric scientist and a known sky-watcher is that I get to notice beautiful moments in the sky. I remember being on a trip with friends and I looked up (as I usually do), and I was gifted with a gorgeous sundog and halo arc. It was such a beautiful moment, and because I noticed it, my friends got to enjoy it too.

Can you share a photo or image from a memorable NASA project you’ve worked on, and tell us a little bit about why the project stood out to you?
I absolutely loved being on the PBS Kids TV Show, SciGirls for their episode SkyGirls! This featured a NASA program called Students’ Clouds Observations On-Line (S’COOL). It was a citizen science program where students from around the globe could take observations of clouds from the ground that coincided with satellite overpasses, and the intention was to help scientists validate (or check) the accuracy of the code they use to detect clouds from satellite measurements. I grew up watching educational programming from PBS, so it was an honor to be a science mentor on a TV show that I knew would reach children across the nation who might be interested in different STEM fields. In this photo, the three young women I worked with on the show and I are talking about the different types of clouds.
To stay up to date on Yolanda's mission and everything going on in NASA Earth science, be sure to follow NASA Earth on Twitter and Facebook.
🌎 If you're looking for Earth Day plans, we have live events, Q&As, scavenger hunts and more going on through April 24. Get the details and register for our events HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
6 Ways NASA is Involved in Climate Science
When it comes to climate change, we play a unique role in observing and understanding changes to the planet. Thanks to NASA’s Earth observations and related research, we know our planet and its climate are changing profoundly. We also know human activities, like releasing carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere, are driving this change.
Not only do we make these observations, we help people and groups use this knowledge to benefit society. The work we do at NASA is critical to helping us understand the ways our planet is responding to increased temperatures.

Here are 6 ways that we are involved in climate science and informing decisions:
1. Monitoring Earth’s vital signs
Just like a doctor checks your vitals when you go in for a visit, here at NASA we are constantly monitoring Earth’s vital signs - carbon dioxide levels, global temperature, Arctic sea ice minimum, the ice sheets and sea level, and more.

We use satellites in space, observations from airplanes and ships, and data collected on the ground to understand our planet and its changing climate. Scientists also use computers to model and understand what's happening now and what might happen in the future.

People who study Earth see that the planet’s climate is getting warmer. Earth's temperature has gone up more than 1 degree Celsius (~2 degrees Fahrenheit) in the last 100 years. This may not seem like much, but small changes in Earth's temperature can have big effects. The current warming trend is of particular significance, because it is predominantly the result of human activity since the mid-20th century and is proceeding at an unprecedented rate.

People drive cars. People heat and cool their houses. People cook food. All those things take energy. Human-produced greenhouse gas emissions are largely responsible for warming our planet. Burning fossil fuels -- which includes coal, oil, and natural gas -- releases greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, where they act like an insulating blanket and trap heat near Earth’s surface.
At NASA, we use satellites and instruments on board the International Space Station to confirm measurements of atmospheric carbon levels. They’ve been increasing much faster than any other time in history.

2. Tracking global land use and its impacts
We also monitor and track global land use. Currently, half the world's population lives in urban areas, and by 2025, the United Nations projects that number will rise to 60%.

With so many people living and moving to metropolitan areas, the scientific world recognizes the need to study and understand the impacts of urban growth both locally and globally.

The International Space Station helps with this effort to monitor Earth. Its position in low-Earth orbit provides variable views and lighting over more than 90% of the inhabited surface of Earth, a useful complement to sensor systems on satellites in higher-altitude polar orbits. This high-resolution imaging of land and sea allows tracking of urban and forest growth, monitoring of hurricanes and volcanic eruptions, documenting of melting glaciers and deforestation, understanding how agriculture may be impacted by water stress, and measuring carbon dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere.
3. Research into the causes of climate change
Being able to monitor Earth’s climate from space also allows us to understand what’s driving these changes.

With the CERES instruments, which fly on multiple Earth satellites, our scientists measure the Earth’s planetary energy balance – the amount of energy Earth receives from the Sun and how much it radiates back to space. Over time, less energy being radiated back to space is evidence of an increase in Earth’s greenhouse effect. Human emissions of greenhouse gases are trapping more and more heat.

NASA scientists also use computer models to simulate changes in Earth’s climate as a result of human and natural drivers of temperature change.

These simulations show that human activities such as greenhouse gas emissions, along with natural factors, are necessary to simulate the changes in Earth’s climate that we have observed; natural forces alone can’t do so.
4. Research into the effects of climate change
Global climate change has already had observable effects on the environment. Glaciers and ice sheets have shrunk, ice on rivers and lakes is breaking up earlier, plant and animal ranges have shifted, and trees are flowering sooner.

The effects of global climate change that scientists predicted are now occurring: loss of sea ice, accelerated sea level rise and longer, more intense heat waves.
Climate modelers have predicted that, as the planet warms, Earth will experience more severe heat waves and droughts, larger and more extreme wildfires, and longer and more intense hurricane seasons on average. The events of 2020 are consistent with what models have predicted: extreme climate events are more likely because of greenhouse gas emissions.

Plants are also struggling to keep up with rising carbon dioxide levels. Plants play a key role in mitigating climate change. The more carbon dioxide they absorb during photosynthesis, the less carbon dioxide remains trapped in the atmosphere where it can cause temperatures to rise. But scientists have identified an unsettling trend – 86% of land ecosystems globally are becoming progressively less efficient at absorbing the increasing levels of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Helping organizations to use all the data and knowledge NASA generates is another part of our job. We’ve helped South Dakota fight West Nile Virus, helped managers across the Western U.S. handle water, helped The Nature Conservancy protect land for shorebirds, and others. We also support developing countries as they work to address climate and other challenges through a 15-year partnership with the United States Agency for International Development.
5. Action on sustainability
Sustainability involves taking action now to enable a future where the environment and living conditions are protected and enhanced. We work with many government, nonprofit, and business partners to use our data and modeling to inform their decisions and actions. We are also working to advance technologies for more efficient flight, including hybrid-electric propulsion, advanced materials, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.

These advances in research and technology will not only bring about positive changes to the climate and the world in which we live, but they will also drive the economic engine of America and our partners in industry, to remain the world-wide leader in flight development.
We partner with the private sector to facilitate the transfer of our research and NASA-developed technologies. Many innovations originally developed for use in the skies above help make life more sustainable on Earth. For example:
Our Earth-observing satellites help farmers produce more with less water.
Expertise in rocket engineering led to a technique that lessens the environmental impact of burning coal.
A fuel cell that runs equipment at oil wells reduces the need to vent greenhouse gases.
6. Applying climate research to preserve NASA centers in coastal areas
Sea level rise in the two-thirds of Earth covered by water may jeopardize up to two-thirds of NASA's infrastructure built within mere feet of sea level.

Some NASA centers and facilities are located in coastal real estate because the shoreline is a safer, less inhabited surrounding for launching rockets. But now these launch pads, laboratories, airfields, and testing facilities are potentially at risk because of sea level rise. We’ve worked internally at NASA to identify climate risks and support planning at our centers.
NASA Climate Science
Climate change is one of the most complex issues facing us today. It involves many dimensions – science, economics, society, politics, and moral and ethical questions – and is a global problem, felt on local scales, that will be around for decades and centuries to come. With our Eyes on the Earth and wealth of knowledge on the Earth’s climate system and its components, we are one of the world’s experts in climate science.
Visit our Climate site to explore and learn more.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
One Hot Year after Another
Globally, 2020 was the hottest year on record, effectively tying 2016, the previous record. Overall, Earth’s average temperature has risen more than 2 degrees Fahrenheit since the 1880s.

Temperatures are increasing due to human activities, specifically emissions of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide and methane.
Heat and the energy it carries are what drive our planet: winds, weather, droughts, floods, and more are expressions of heat. The right amount of heat is even one of the things that makes life on Earth possible. But too much heat is changing the way our planet’s systems act.
My World’s on Fire
Higher temperatures drive longer, more intense fire seasons. As rain and snowfall patterns change, some regions are getting drier and more vulnerable to damage, setting the stage for more fires.

2020 saw several record-breaking fires, both in Australia in the beginning of the year, and in the western U.S. through northern summer and fall. Smoke from fires in both regions reached so high into the atmosphere that it formed clouds and continues to travel around the globe today.

In the Siberian Arctic, unusually high temperatures helped drive at least 19 fires in the region. More than half of them were burning peat soil -- decomposed organic materials -- that stores a lot of carbon. Peat fires release vast amounts of carbon into the atmosphere, potentially leading to even more warming.

The Water’s Getting Warm
It wasn’t just fire seasons setting records. 2020 had more named tropical storms in the Atlantic and more storms making landfall in the U.S. than any hurricane season on record.

Hurricanes rely on warm ocean water as fuel, and this year, the Atlantic provided. 30 named storms weren’t the only things that made this year’s hurricane season notable.

Storms like Eta, Delta, and Iota quickly changed from smaller, weaker tropical storms into more destructive hurricanes. This rapid intensification is complicated, but it’s likely that warmer, more humid weather -- a result of climate change -- helps drive it.

The Ice Is Getting Thin
Add enough heat, and even the biggest chunk of ice will melt. That’s true whether we’re talking about the ice cubes in your glass or the vast sheets of ice at our planet’s poles. Right now, the Arctic region is warming about three times faster than the rest of our planet, which has some major effects both locally and globally.

This year, Arctic sea ice hit a near-record low. Sea ice is actually made of frozen ocean water, and it grows and thaws with the seasons, typically reaching an annual minimum extent in September.

Warmer ocean water led to more ice melting this year, and 2020’s annual minimum extent continued a long trend of shrinking Arctic sea ice extent.
A Long Trend
We study Earth and how it’s changing from the ground, the sky, and space. Using data from sensors all around the planet, we calculate the global average temperature, working with our partners at NOAA.
Many other organizations also track global temperature using their own instruments and methods, and they all match remarkably well. The last seven years were the hottest seven years on record. Earth is getting warmer.

We also study the effects of increasing temperatures, like the melting sea ice and longer fire seasons mentioned above. Additionally, we can study the cause of climate change from space, with a bird’s eye view of increasing carbon in the atmosphere.

The planet is changing because of human activities. We’re working together with other agencies to monitor changes and understand what this means for people in the future.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Check out tiny-house-looking satellite Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich
It might look like something you’d find on Earth, but this piece of technology has a serious job to do: track global sea level rise with unprecedented accuracy. It’s #SeeingTheSeas mission will:
Provide information that will help researchers understand how climate change is reshaping Earth's coastlines – and how fast this is happenin.
Help researchers better understand how Earth's climate is changing by expanding the global atmospheric temperature data record
Help to improve weather forecasts by providing meteorologists information on atmospheric temperature and humidity.
Tune in tomorrow, Nov. 21 at 11:45 a.m. EST to watch this U.S.-European satellite launch to space! Liftoff is targeted for 12:17 p.m. EST. Watch HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How do you guys help with climate change?
Are there any parts of the Earth still left unexplored?
Looking 50 Years in the Future with NASA Earth Scientists
In the 50 years since the first Earth Day, the view from space has revolutionized our understanding of Earth’s interconnected atmosphere, oceans, freshwater, ice, land, ecosystems and climate that have helped find solutions to environmental challenges.
If NASA’s Earth science has changed this much in 50 years, what will it look like in 50 more years?
We asked some researchers what they thought. Here are their answers, in their own words.

Mahta Moghaddam is a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Southern California. She’s building a system that helps sensors sync their measurements.
I am interested in creating new ways to observe the Earth. In particular, my team and I are building and expanding a system that will allow scientists to better study soil moisture. Soil moisture plays a vital role in the water and energy cycle and drives climate and weather patterns. When soil is wet and there is enough solar radiation, water can evaporate and form clouds, which precipitate back to Earth. Soil also feeds us – it nourishes our crops and sustains life on Earth. It’s one of the foundations of life! We need to characterize and study soil in order to feed billions of people now and in the future.

Our novel tool aims to observe changes in soil moisture using sensors that talk to each other and make decisions in real time. For instance, if one sensor in a crop field notes that soil is dry in a plot, it could corroborate it with other sensors in the area and then notify a resource manager or decision maker that an area needs water. Or if a sensor in another location senses that soil moisture is changing quickly due to rain or freeze/thaw activity, it could send a command to launch a drone or even to notify satellites to start observing a larger region. We live in one big, connected world, and can and will use many different scales of observations – local to global – from point-scale in-situ sensors to the scales that can be covered by drones, airplanes, and satellites. In just a few years from now, we might see much more vastly automated systems, with some touching not only Earth observations, but other parts of our lives, like drone deliveries of medical tests and supplies.

Odele Coddington is a scientist at the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado, Boulder. She’s building an instrument to measure how much solar energy Earth reflects back into space.
My research is focused on the Earth system response to the Sun’s energy. I spend half of my time thinking about the amount and variability of the Sun’s energy, also known as the solar irradiance. I’m particularly interested in the solar spectral irradiance, which is the study of the individual wavelengths of the Sun’s energy, like infrared and ultraviolet. On a bright, clear day, we feel the Sun’s warmth because the visible and infrared radiation penetrate Earth’s atmosphere to reach the surface. Without the Sun, we would not be able to survive. Although we’ve been monitoring solar irradiance for over 40 years, there is still much to learn about the Sun’s variability. Continuing to measure the solar irradiance 50 years from now will be as important as it is today.

I spend the other half of my time thinking about the many processes driven by the Sun’s energy both within the atmosphere and at the surface. I’m excited to build an instrument that will measure the integrated signal of these processes in the reflected solar and the emitted thermal radiation. This is my first foray into designing instrumentation and it has been so invigorating scientifically. My team is developing advanced technology that will measure Earth’s outgoing radiation at high spatial resolution and accuracy. Our instrument will be small from the onset, as opposed to reducing the size and mass of existing technology. In the future, a constellation of these instruments, launched on miniaturized spacecraft that are more flexible to implement in space, will give us more eyes in the sky for a better understanding of how processes such as clouds, wildfires and ice sheet melting, for instance, alter Earth’s outgoing energy.

Sujay Kumar is a research physical scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. He works on the Land Information System.
Broadly, I study the water cycle, and specifically the variability of its components. I lead the development of a modeling system called the Land Information System that isolates the land and tries to understand all the processes that move water through the landscape. We have conceptual models of land surface processes, and then we try to constrain them with satellite data to improve our understanding. The outputs are used for weather and climate modeling, water management, agricultural management and some hazard applications.

I think non-traditional and distributed platforms will become more the norm in the future. So that could be things like CubeSats and small sats that are relatively cheaper and quicker than large satellites in terms of how much time it takes to design and launch. One of the advantages is that because they are distributed, you’re not relying on a single satellite and there will be more coverage. I also think we’ll be using data from other “signals of opportunity” such as mobile phones and crowd-sourced platforms. People have figured out ways to, for example, retrieve Earth science measurements from GPS signals.
I feel like in the future we will be designing our sensors and satellites to be adaptive in terms of what the observational needs on the ground are. Say a fire or flood happens, then we will tell the satellite to look over there more intensely, more frequently so that we can benefit. Big data is a buzzword, but it’s becoming a reality. We are going to have a new mission call NISAR that’s going to collect so much data that we really have to rethink how traditional modeling systems will work. The analogy I think of is the development of a self-driving car, which is purely data driven, using tons and tons of data to train the model that drives the car. We could possibly see similar things in Earth science.
Hear from more NASA scientists on what they think the future will bring for Earth science:
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Participate in the 50th anniversary of Earth Day by asking our experts anything about NASA’s role in Earth Science!
This year marks the 50th anniversary of Earth Day, and to commemorate the big day we’re bringing you exclusive access our Acting Director of Earth Sciences, Sandra Cauffman, and Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, Dr. Thomas Zurbuchen! They will be teaming up to take your questions in an Answer Time session on Earth Day, April 22, from 12-1pm EDT here on NASA’s Tumblr! Make sure to ask your question now by visiting http://nasa.tumblr.com/ask!
Our investment in space – both the unique Earth science we conduct from orbit and the technology we’ve developed by living in space and exploring our solar system and universe – is returning benefits every day to people around the world, particularly those who are working on environmental issues. From documenting Earth’s changing climate to creating green technologies to save energy and natural resources, we’re working to help us all live more sustainably on our home planet and adapt to natural and human-caused changes.

NASA Earth Science Fun Facts!
From space we study: dust storms, volcanoes, flooding, coral reefs, night lights, wildfires, urban growth, food production, mosquito tracking and other human health issues, precipitation across the world, hurricanes and typhoons, soil moisture, land and sea ice, and changes to the land and sea surfaces.
From airborne research planes we track: changes in polar ice, glaciers, sea level rise, cloud formation, storms, sea level rise and Earth’s changing landscape.
Our Earth science focus areas include: Atmospheric Composition, Weather and Atmospheric Dynamics, Climate Variability and Change, Water and Energy Cycle, Carbon Cycle and Ecosystems, Earth Surface and Interior
Keep up to date with all our Earth Science missions and research by following NASA Earth on Twitter, Facebook and Instagram.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Are We Alone? How NASA Is Trying to Answer This Question.
One of the greatest mysteries that life on Earth holds is, “Are we alone?”

At NASA, we are working hard to answer this question. We’re scouring the universe, hunting down planets that could potentially support life. Thanks to ground-based and space-based telescopes, including Kepler and TESS, we’ve found more than 4,000 planets outside our solar system, which are called exoplanets. Our search for new planets is ongoing — but we’re also trying to identify which of the 4,000 already discovered could be habitable.

Unfortunately, we can’t see any of these planets up close. The closest exoplanet to our solar system orbits the closest star to Earth, Proxima Centauri, which is just over 4 light years away. With today’s technology, it would take a spacecraft 75,000 years to reach this planet, known as Proxima Centauri b.
How do we investigate a planet that we can’t see in detail and can’t get to? How do we figure out if it could support life?
This is where computer models come into play. First we take the information that we DO know about a far-off planet: its size, mass and distance from its star. Scientists can infer these things by watching the light from a star dip as a planet crosses in front of it, or by measuring the gravitational tugging on a star as a planet circles it.
We put these scant physical details into equations that comprise up to a million lines of computer code. The code instructs our Discover supercomputer to use our rules of nature to simulate global climate systems. Discover is made of thousands of computers packed in racks the size of vending machines that hum in a deafening chorus of data crunching. Day and night, they spit out 7 quadrillion calculations per second — and from those calculations, we paint a picture of an alien world.

While modeling work can’t tell us if any exoplanet is habitable or not, it can tell us whether a planet is in the range of candidates to follow up with more intensive observations.

One major goal of simulating climates is to identify the most promising planets to turn to with future technology, like the James Webb Space Telescope, so that scientists can use limited and expensive telescope time most efficiently.

Additionally, these simulations are helping scientists create a catalog of potential chemical signatures that they might detect in the atmospheres of distant worlds. Having such a database to draw from will help them quickly determine the type of planet they’re looking at and decide whether to keep observing or turn their telescopes elsewhere.
Learn more about exoplanet exploration, here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
2019 Temperature By the Numbers
The Year
2nd Hottest
2019 was the second-hottest year since modern record keeping began. NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration work together to track temperatures around the world and study how they change from year to year. For decades, the overall global temperature has been increasing.

Over the long term, world temperatures are warming, but each individual year is affected by things like El Niño ocean patterns and specific weather events.
The global temperature is an average, so not every place on Earth had its second-warmest year. For instance, the continental U.S. had a cold October, but Alaska set records for high temperatures. The U.S. was still warmer than average over the year.
Globally, Earth’s temperature in 2019 was more than 2°F warmer than the late 19th Century.
The Record
140 years
Since 1880, we can put together a consistent record of temperatures around the planet and see that it was much colder in the late-19th century. Before 1880, uncertainties in tracking global temperatures are larger. Temperatures have increased even faster since the 1970s, the result of increasing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.

10 years
The last decade was the hottest decade on record.

20,000 Individual Observations
Scientists from NASA use data from more than 20,000 weather stations and Antarctic research stations, together with ship- and buoy-based observations of sea surface temperatures to track global temperatures.

The Consequences
90%
As Earth warms, polar ice is melting at an accelerated rate. The Arctic is warming even faster than the rest of the planet. This northern summer, 90% of the surface of the Greenland Ice Sheet melted.

8 inches
Melting ice raises sea levels around the world. While ice melts into the ocean, heat also causes the water to expand. Since 1880, sea levels globally have risen approximately 8 inches, although regional rates of sea level rise can be even higher.

100+ fires
As temperatures increase, fire seasons burn hotter and longer. During June and July 2019, more than 100 long-lived and intense wildfires burned north of the Arctic circle. This year also saw intense, record-setting fires in Australia.


46% increase in CO2 levels
This decades-long warming trend is the result of increasing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, released by human activities.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Moving at the Speed of Arctic Ice
Time-lapses taken from space can help track how Earth’s polar regions are changing, watching as glaciers retreat and accelerate, and ice sheets melt over decades.

Using our long data record and a new computer program, we can watch Alaskan glaciers shift and flow every year since 1972. Columbia Glacier, which was relatively stable in the 1970s, has since retreated rapidly as the climate continues to warm.

The Malaspina Glacier has pulsed and spread and pulsed again. The flashes and imperfect frames in these time-lapses result from the need for cloud-free images from each year, and the technology limitations of the early generation satellites.

In Greenland, glaciers are also reacting to the warming climate. Glaciers are essentially frozen rivers, flowing across land. As they get warmer, they flow faster and lose more ice to the ocean. On average, glaciers in Greenland have retreated about 3 miles between 1985 and 2018. The amount of ice loss was fairly consistent for the first 15 years of the record, but started increasing around 2000.

Warmer temperatures also affect Greenland farther inland, where the surface of ice sheets and glaciers melts, forming lakes that can be up to 3 miles across. Over the last 20 years, the number of meltwater lakes forming in Greenland increased 27% and appeared at higher elevations, where temperatures were previously too cold for melt.

Whether they're studying how ice flows into the water, or how water pools atop ice, scientists are investigating some of the many aspects of how climate affects Earth's polar regions.
For more information, visit climate.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Smoke Gets In Your Eyes…and Our Instruments
Fires are some of the most dynamic and dramatic natural phenomena. They can change rapidly, burning natural landscapes and human environments alike. Fires are a natural part of many of Earth’s ecosystems, necessary to replenish soil and for healthy plant growth. But, as the planet warms, fires are becoming more intense, burning longer and hotter.

Right now, a fleet of vehicles and a team of scientists are in the field, studying how smoke from those fires affects air quality, weather and climate. The mission? It’s called FIREX-AQ. They’re working from the ground up to the sky to measure smoke, find out what’s in it, and investigate how it affects our lives.

Starting on the ground, the Langley Aerosol Research Group Experiment (LARGE) operates out of a large van. It’s one of two such vans working with the campaign, along with some other, smaller vans. It looks a little like a food truck, but instead of a kitchen, the inside is packed full of science instruments.

The team drives the van out into the wilderness to take measurements of smoke and tiny particles in the air at the ground level. This is important for a few reasons: First of all, it’s the stuff we’re breathing! It also gives us a look at smoke overnight, when the plumes tend to sink down out of the atmosphere and settle near the ground until temperatures heat back up with the Sun. The LARGE group camps out with their van full of instruments, taking continuous measurements of smoke…and not getting much sleep.

Just a little higher up, NOAA’s Twin Otter aircraft can flit down close to where the fires are actually burning, taking measurements of the smoke and getting a closer look at the fires themselves. The Twin Otters are known as “NOAA’s workhorses” because they’re easily maneuverable and can fly nice and slow to gather measurements, topping out at about 17,000 feet.

Then, sometimes flying at commercial plane height (30,000 feet) and swooping all the way down to 500 feet above the ground, NASA’s DC-8 is packed wing to wing with science instruments. The team onboard the DC-8 is looking at more than 500 different chemicals in the smoke.

The DC-8 does some fancy flying, crisscrossing over the fires in a maneuver called “the lawnmower” and sometimes spiraling down over one vertical column of air to capture smoke and particles at all different heights. Inside, the plane is full of instrument racks and tubing, capturing external air and measuring its chemical makeup. Fun fact: The front bathroom on the DC-8 is closed during science flights to make sure the instruments don’t accidentally measure anything ejected from the plane.

Finally, we make it all the way up to space. We’ve got a few different mechanisms for studying fires already mounted on satellites. Some of the satellites can see where active fires are burning, which helps scientists and first responders keep an eye on large swaths of land.

Some satellites can see smoke plumes, and help researchers track them as they move across land, blown by wind.

Other satellites help us track weather and forecast how the fires might behave. That’s important for keeping people safe, and it helps the FIREX-AQ team know where to fly and drive when they’ll get the most information. These forecasts use computer models, based on satellite observations and data about how fires and smoke behave. FIREX-AQ’s data will be fed back into these models to make them even more accurate.

Learn more about how NASA is studying fires from the field, here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Polar Vortex spills Arctic weather into North America

What in the world is a polar vortex? On Earth, it’s a large area of low pressure and extremely cold air that usually swirls over the Arctic, with strong counter-clockwise winds that trap the cold around the Pole. But disturbances in the jet stream and the intrusion of warmer mid-latitude air masses can disturb this polar vortex and make it unstable, sending Arctic air south into middle latitudes.
That has been the case in late January 2019 as frigid weather moves across the Midwest and Northern Plains of the United States, as well as interior Canada. Forecasters are predicting that air temperatures in parts of the continental United States will drop to their lowest levels since at least 1994, with the potential to break all-time record lows for January 30 and 31. With clear skies, steady winds, and snow cover on the ground, as many as 90 million Americans could experience temperatures at or below 0 degrees Fahrenheit (-18° Celsius), according to the National Weather Service (NWS).
The Goddard Earth Observing System Model above shows this air temperature movement at 2 meters (around 6.5 feet above the ground) from January 23-29. You can see some portions of the Arctic are close to the freezing point—significantly warmer than usual for the dark of mid-winter—while masses of cooler air plunge toward the interior of North America.

Science Behind the Polar Vortex / Credit: NOAA
Meteorologists predicted that steady northwest winds (10 to 20 miles per hour) were likely to add to the misery, causing dangerous wind chills below -40°F (-40°C) in portions of 12 states. A wind chill of -20°F can cause frostbite in as little as 30 minutes, according to the weather service.
Not sure how cold that is? Check out the low temperatures on January 30, 2019 in some of the coldest places on Earth—and a planetary neighbor:
-46°F (-43°C) -- Chesterfield, Newfoundland
-36°F (-33°C) -- Yukon Territory, Canada
-33°F (-27°C) -- Fargo, North Dakota (Within the Polar Vortex)
-28°F (-18°C) -- Minneapolis, Minnesota (Within the Polar Vortex)
-27°F (-33°C) -- Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station, Antarctica
-24°F (-31°C) -- Chicago, Illinois (Within the Polar Vortex)
-15°F (5°C) -- Barrow, Alaska
-99°F (-73°C) -- Mars
Learn more about the science behind the polar vortex and how NASA is modeling it here: https://go.nasa.gov/2Wtmb43.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
NASA Science Show & Tell
This week, we’re at one of the biggest science conferences in the country, where our scientists are presenting new results from our missions and projects. It’s called the American Geophysical Union’s Fall Meeting.
Here are a few of the things we shared this week...

The Sun
A few months into its seven-year mission, Parker Solar Probe has already flown far closer to the Sun than any spacecraft has ever gone. The data from this visit to the Sun has just started to come back to Earth, and scientists are hard at work on their analysis.

Parker Solar Probe sent us this new view of the Sun’s outer atmosphere, the corona. The image was taken by the mission’s WISPR instrument on Nov. 8, 2018, and shows a coronal streamer seen over the east limb of the Sun. Coronal streamers are structures of solar material within the Sun's atmosphere, the corona, that usually overlie regions of increased solar activity. The fine structure of the streamer is very clear, with at least two rays visible. Parker Solar Probe was about 16.9 million miles from the Sun's surface when this image was taken. The bright object near the center of the image is Mercury, and the dark spots are a result of background correction.
Hurricane Maria
Using a satellite view of human lights, our scientists watched the lights go out in Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria. They could see the slow return of electricity to the island, and track how rural and mountainous regions took longer to regain power.

In the spring, a team of scientists flew a plane over Puerto Rico’s forests, using a laser instrument to measure how trees were damaged and how the overall structure of the forests had changed.

Earth’s Ice
Our scientists who study Antarctica saw some surprising changes to East Antarctica. Until now, most of the continent’s melting has been on the peninsula and West Antarctica, but our scientists have seen glaciers in East Antarctica lose lots of ice in the last few years.


Our ICESat-2 team showed some of their brand new data. From the changing height of Antarctic ice to lagoons off the coast of Mexico, the little satellite has spent its first few months measuring our planet in 3D. The laser pulses even see individual ocean waves, in this graph.

Scientists are using our satellite data to track Adélie penguin populations, by using an unusual proxy -- pictures of their poop! Penguins are too small to be seen by satellites, but they can see large amounts of their poop (which is pink!) and use that as a proxy for penguin populations.

Asteroid Bennu
Our OSIRIS-REx mission recently arrived at its destination, asteroid Bennu. On approach, data from the spacecraft’s spectrometers revealed chemical signatures of water trapped in clay minerals. While Bennu itself is too small to have ever hosted liquid water, the finding indicates that liquid water was present at some time on Bennu’s parent body, a much larger asteroid.
We also released a new, detailed shape model of Bennu, which is very similar to our ground-based observations of Bennu’s shape. This is a boon to ground-based radar astronomy since this is our first validation of the accuracy of the method for an asteroid! One change from the original shape model is the size of the large boulder near Bennu’s south pole, nicknamed “Benben.” The boulder is much bigger than we thought and overall, the quantity of boulders on the surface is higher than expected. Now the team will make further observations at closer ranges to more accurately assess where a sample can be taken on Bennu to later be returned to Earth.

Jupiter
The Juno mission celebrated it’s 16th science pass of #Jupiter, marking the halfway point in data collection of the prime mission. Over the second half of the prime mission — science flybys 17 through 32 — the spacecraft will split the difference, flying exactly halfway between each previous orbit. This will provide coverage of the planet every 11.25 degrees of longitude, providing a more detailed picture of what makes the whole of Jupiter tick.

Mars
The Mars 2020 team had a workshop to discuss the newly announced landing site for our next rover on the Red Planet. The landing site...Jezero Crater! The goal of Mars 2020 is to learn whether life ever existed on Mars. It's too cold and dry for life to exist on the Martian surface today. But after Jezero Crater formed billions of years ago, water filled it to form a deep lake about the same size as Lake Tahoe. Eventually, as Mars' climate changed, Lake Jezero dried up. And surface water disappeared from the planet.
Interstellar Space
Humanity now has two interstellar ambassadors. On Nov. 5, 2018, our Voyager 2 spacecraft left the heliosphere — the bubble of the Sun’s magnetic influence formed by the solar wind. It’s only the second-ever human-made object to enter interstellar space, following its twin, Voyager 1, that left the heliosphere in 2012.

Scientists are especially excited to keep receiving data from Voyager 2, because — unlike Voyager 1 — its plasma science instrument is still working. That means we’ll learn brand-new information about what fills the space between the stars.
Learn more about NASA Science at science.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Uncovering a Massive Meteor Crater Found Lurking Under the Ice

For the first time ever, we've found a massive crater hiding under one of Earth's ice sheets. Likely caused by a meteor, it was uncovered in Greenland by a team of international scientists using radar data.

The data was collected by missions like our Operation IceBridge, which flies planes over Greenland and Antarctica to study the ice and snow at our planet’s poles.

In this case, the crater is near Hiawatha Glacier, covered by a sheet of ice more than half a mile thick. We're pretty sure that the crater was caused by a meteor because it has characteristics traditionally associated with those kinds of impacts, like a bowl shape and central peaks.

It’s also one of the 25 largest impact craters in the world, large enough to hold the cities of Paris or Washington, D.C. The meteor that created it was likely half a mile wide.

Currently, there’s still lots to learn about the crater – and the meteor that created it – but it’s likely relatively young in geologic timescales. The meteor hit Earth within the last 3 million years, but the impact could have been as recent as 13,000 years ago.

While it was likely smaller than the meteor credited with knocking out the dinosaurs, this impact could have potentially caused a large influx of fresh water into the northern Atlantic Ocean, which would have had profound impacts for life in the region at the time.

Go here to learn more about this discovery: https://www.nasa.gov/press-release/international-team-nasa-make-unexpected-discovery-under-greenland-ice

Operation IceBridge continues to uncover the hidden secrets under Earth's ice. IceBridge has been flying for 10 years, providing a data bridge between ICESat, which flew from 2003 to 2009, and ICESat-2, which launched in September. IceBridge uses a suite of instruments to help track the changing height and thickness of the ice and the snow cover above it. IceBridge also measures the bedrock below the ice, which allows for discoveries like this crater.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Packing for a Journey into the Twilight Zone
Submitted for your consideration: A team of researchers from more than 20 institutions, boarding two research vessels, heading into the ocean’s twilight zone.
The twilight zone is a dimly lit region between 650 and 3300 feet below the surface, where we’re unfolding the mystery of how tiny ocean organisms affect our planet’s climate.

These tiny organisms – called phytoplankton – are plant-like and mostly single-celled. They live in water, taking in carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen.

Two boats, more than 100 researchers from more than 20 partner institutions, and a whole fleet of robotic explorers make up the EXport Processes in the Ocean from RemoTe Sensing (EXPORTS) team. We’re learning more about what happens to carbon dioxide after phytoplankton digest it.

The Equipment to Find Phytoplankton

Phytoplankton have predators in the ocean called zooplankton. They absorb the phytoplankton’s carbon, carrying it up the food chain. The EXPORTS mission will focus partly on how that happens in the ocean’s twilight zone, where some zooplankton live. When phytoplankton die, sometimes their bodies sink through the same area. All of this carries carbon dioxide into the ocean’s depths and out of Earth’s atmosphere.

Counting Life
Studying the diversity of these organisms is important to better understand what’s happening to the phytoplankton as they die. Researchers from the Virginia Institute of Marine Science are using a very fine mesh net to sample water at various depths throughout the ocean to count various plankton populations.

Researchers from the University of Rhode Island are bringing the tools to sequence the DNA of phytoplankton and zooplankton to help count these organism populations, getting a closer look at what lives below the ocean’s surface.

Science at 500 Feet
Taking measurements at various depths is important, because phytoplankton, like plants, use sunlight to digest carbon dioxide. That means that phytoplankton at different levels in the ocean absorb and digest carbon differently. We’re bringing a Wirewalker, an instrument that glides up and down along a vertical wire to take in water samples all along its 500-foot long tether.

This journey to the twilight zone will take about thirty days, but we’ll be sending back dispatches from the ships. Follow along as we dive into ocean diversity on our Earth Expeditions blog: https://blogs.nasa.gov/earthexpeditions.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Studying the tiny life of phytoplankton
Phytoplankton. Have you ever heard of them? At NASA, these tiny organisms are kind of a big deal.

Biodiversity in the ocean is a delicate, but essential balance for life on Earth. One way NASA studies this balance is by observing phytoplankton – microalgae that contain chlorophyll, require light to grow, and form the base of the marine food chain.
Phytoplankton even have an essential role in an upcoming NASA mission.
This mission is called PACE- "Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem.” It will reveal interactions between the ocean and atmosphere, including how they exchange carbon dioxide and how atmospheric aerosols might fuel phytoplankton growth in the surface ocean.
Here are four areas main areas the mission will focus on as part of #WorldOceansMonth.
1. Harmful algal blooms: Not the good kind of bloom
The word “bloom” sounds pretty, but harmful algal blooms (HABs) are anything but.
When an ocean region is rich in nutrients – think of it as adding fertilizer to the ocean - phytoplankton such as cyanobacteria multiply much faster than usual. This is called a “bloom.”
Some blooms are smelly and ugly but harmless. Others, like HABs, release toxins into the water that can make fish, shellfish, turtles and even humans very sick.
NASA’s PACE mission will help track phytoplankton growth and ocean health to make sure all of us stay healthy, balanced and blooming. In a good way.
2. Aerosols: The sea-sky connection
What do phytoplankton and clouds have in common? More than you might think.
PACE will also study aerosols, which are any particles or droplets suspended in our atmosphere. Humans create aerosols, like soot or car exhaust, but some phytoplankton release aerosols too.
For example, dust – also an aerosol – can blow into the ocean, depositing iron that helps phytoplankton grow. These phytoplankton then release dimethyl sulfide, a gas that turns into an aerosol, which can influence how clouds form.
Whether the aerosols in our atmosphere come from the ocean or land, it’s important to know how they are impacting our environment. PACE will help clear up some of our questions about what is in our air.
3. Biodiversity: The more, the merrier
A healthy ocean supports healthy industries and economies, contributes to a healthy atmosphere and helps keep plants, animals and humans healthy and happy. One key to a healthy, balanced ocean is lots of biodiversity.
Biodiversity means having a wide variety of plant and animal species in an ecosystem. It’s important to have many different species of phytoplankton, because each species plays a different role in processing carbon, providing food for tiny animals, and keeping the ocean healthy.
PACE will track the size and movements of phytoplankton populations from space to help our seas stay diverse and bountiful.
4. Fisheries: Phytoplankton feed fish feed friends
One simple reason for tracking the ocean’s health is that fish eat tiny animals that eat phytoplankton, and people eat fish.
Fisheries and aquaculture support about 12 percent of jobs around the world, including employing more than 3 million people in the United States. By better understanding our ocean’s health and how it might change in the future, we can make predictions about impacts to our economies and food supply.
To learn more about phytoplankton, visit our website.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.