BugsFeed: 7 Bad Ass Organisms That Can Survive Intracellularly In Immune Cells
BugsFeed: 7 bad ass organisms that can survive intracellularly in immune cells
1. Mycobacterium tuberculosis - Stops fusion!

Mycobacterium tuberculosis utilizes macrophages for its replication! (It uses the usual killer to expand it’s army :O ) How does tuberculosis bacilli survive in macrophages? M. tuberculosis has evolved a number of very effective survival strategies - It inhibits phagosome-lysosome fusion and inhibits phagosome acidification ensuring it’s survival inside the macrophage.
2. Brucella - Has chains, like Bruce Lee.

Brucella has a LPS O-chain. It ensures the Brucella containing vacuole (BCV) avoids fusion with lysosomes, prevents the deposition of complement at the bacterial surface and forms stable large clusters with MHC-II named macrodomians in the cell surface, interfering with MHC-II presentation of peptides to specific CD4+ T cells. Woah.
3. Listeria - It gets internalized in a vacuole and then runs away.

The pore-forming protein listeriolysin O mediates escape from host vacuoles. Once in the cytosol, the L. monocytogenes mediates efficient actin-based motility, thereby propelling the bacteria into neighboring cells. The cytosol is a favorable environment for listeria’s growth.
4. Mycobacterium leprae - Cholesterol and TACO!

Mycobacterium leprae is able to induce lipid droplet formation in infected macrophages. Cholesterol mediates the recruitment of TACO from the plasma membrane to the phagosome. TACO, also termed as coronin-1A (CORO1A), is a coat protein that prevents phagosome-lysosome fusion and thus degradation of mycobacteria in lysosomes. The entering of mycobacteria at cholesterol-rich domains of the plasma membrane and their subsequent uptake in TACO-coated phagosomes promotes intracellular survival.
5. Coxiella brunetti - The indestrucible

This hardy, obligate intracellular pathogen has evolved to not only survive, but to thrive, in the harshest of intracellular compartments: the phagolysosome. Following internalization, the nascent Coxiella phagosome ultimately develops into a large and spacious parasitophorous vacuole (PV) that acquires lysosomal characteristics such as acidic pH, acid hydrolases and cationic peptides, defences designed to rid the host of intruders.
6. Salmonella - TTSS

Salmonella have a specialized secretion system, termed the type III secretion system (TTSS), as well as proteins secreted by this system, are encoded in Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI1). TTSS are used by bacterial pathogens to inhibit their phagocytosis, induce eukaryotic cell death, and alter the host cell cytoskeleton. Salmonella species have at least one other TTSS encoded on SPI2 that appears to be involved in intracellular survival.
7. Human Immunodeficiency Virus - Tries to not attract attention

After infecting cells, HIV survives. Ever wondered why? It’s because the HIV protein, Nef plays a role in downregulating the expression of various proteins needed for recognition by potentially dangerous CD8 T cells. Nef lowers the surface expression of CD4, and several haplotypes of MHC-I by redirecting their transport from the trans-Golgi network. Another gene, Tat, appears to upregulate the expression of Bcl-2 during the early phase of cellular infection, increasing the likelihood that it will receive survival signals.
Many viruses can survive intracellularly, but I’ve included specifically HIV in this list because it survives in immune cells and it is an important virus to know.
For appropriate sources and references, click here.
More Posts from Fuadalanazi and Others

يالله 💙
Penicillin

Penicillin is a widely used antibiotic prescribed to treat staphylococci and streptococci bacterial infections.
beta-lactam family
Gram-positive bacteria = thick cell walls containing high levels of peptidoglycan
gram-negative bacteria = thinner cell walls with low levels of peptidoglycan and surrounded by a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) layer that prevents antibiotic entry
penicillin is most effective against gram-positive bacteria where DD-transpeptidase activity is highest.
Examples of penicillins include:
amoxicillin
ampicillin
bacampicillin
oxacillin
penicillin
Mechanism(s)
Penicillin inhibits the bacterial enzyme transpeptidase, responsible for catalysing the final peptidoglycan crosslinking stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Cells wall is weakened and cells swell as water enters and then burst (lysis)
Becomes permanently covalently bonded to the enzymes’s active site (irreversible)


Alternative theory: penicillin mimics D-Ala D-Ala

Or may act as an umbrella inhibitor

Resistance
production of beta-lactamase - destroys the beta-lactam ring of penicillin and makes it ineffective (eg Staphylococcus aureus - most are now resistant)
In response, synthetic penicillin that is resistant to beta-lactamase is in use including egdicloxacillin, oxacillin, nafcillin, and methicillin.
Some is resistant to methicillin - methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Demonstrating blanket resistance to all beta-lactam antibiotics -extremely serious health risk.
مقطع رائع وخاشع للقارئ يوسف ابكر من سورة التوبة (by samel945)
الشيخ عبد الباسط عبد الصمد(التكوير و سورة القدر)روعة (by theeslamcena)



Cone snails might not seem like deadly predators, especially when you consider how easily a fish could outswim them. However, these snails await the cover of darkness to prey on sleeping fish. They appear to release paralyzing chemicals before using a venomous barb to finally put the fish out of its misery. (Source)

“Sequence VR" was exhibited at the V & A Museum in London, as part of the London Design Festival. A new immersive virtual reality experience has been created using an Oculus Rift as part of “Sequence” using the data and footage from the project. It was shown alongside a series of objects and artefacts created during the project including live bacteria. The exhibit was accompanied by a participatory DNA extraction/preparation workshop where Dumitriu was joined by Dr Nicola Fawcett from the Modernisng Medical Microbiology Project. The event took place on 25th - 27th September 2015. See more information here.

No bacterium is an island.
Many people think of bacteria as tiny Lone Rangers, paddling their flagellar canoes across the desolate petri dish sea. But in “the wild”, bacteria exist as complex, interwoven, constantly competing social communities.
Every scoop of soil is a battlefield of chemical chatter. Species send out molecular messages-in-a-bottle that ride the waves of diffusion to their mates. Some even thread electrical cables between neighboring cells. Now, new research has identified elaborate shared membranes that let single cells swarm as a superorganism …
Check out my latest article for Wired all about a soil bacterium named Myxococcus xanthus. It’s under everyone’s feet right now, and it has developed one of the most elaborate physical webs ever witnessed in bacteria. That’s it up top, devouring a colony of E. coli using its patented rippling wave attack.
It’s a stealth communication network that lets them hunt like a tiny wolfpack. So cool. Plus I got to use a GIF, so double win.
Once you’re done with that, check out this great TED talk from Bonnie Bassler all about how bacteria communicate.
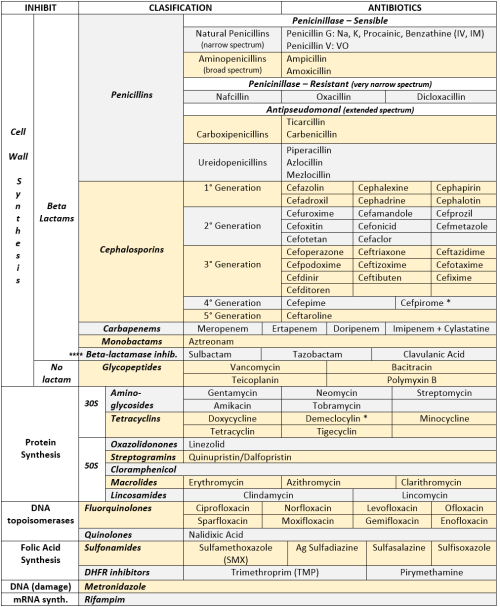
ANTIBIOTICS CHEAT SHEET :)
Also, REMEMBER!!!!
* Sulfonamides compete for albumin with:
Bilirrubin: given in 2°,3°T, high risk or indirect hyperBb and kernicterus in premies
Warfarin: increases toxicity: bleeding
* Beta-lactamase (penicinillase) Suceptible:
Natural Penicillins (G, V, F, K)
Aminopenicillins (Amoxicillin, Ampicillin)
Antipseudomonal Penicillins (Ticarcillin, Piperacillin)
* Beta-lactamase (penicinillase) Resistant:
Oxacillin, Nafcillin, Dicloxacillin
3°G, 4°G Cephalosporins
Carbapenems
Monobactams
Beta-lactamase inhibitors
* Penicillins enhanced with:
Clavulanic acid & Sulbactam (both are suicide inhibitors, they inhibit beta-lactamase)
Aminoglycosides (against enterococcus and psedomonas)
* Aminoglycosides enhanced with Aztreonam
* Penicillins: renal clearance EXCEPT Oxacillin & Nafcillin (bile)
* Cephalosporines: renal clearance EXCEPT Cefoperazone & Cefrtriaxone (bile)
* Both inhibited by Probenecid during tubular secretion.
* 2°G Cephalosporines: none cross BBB except Cefuroxime
* 3°G Cephalosporines: all cross BBB except Cefoperazone bc is highly highly lipid soluble, so is protein bound in plasma, therefore it doesn’t cross BBB.
* Cephalosporines are "LAME“ bc they do not cover this organisms
L isteria monocytogenes
A typicals (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia)
M RSA (except Ceftaroline, 5°G)
E nterococci

* Disulfiram-like effect: Cefotetan & Cefoperazone (mnemonic)
* Cefoperanzone: all the exceptions!!!
All 3°G cephalosporins cross the BBB except Cefoperazone.
All cephalosporins are renal cleared, except Cefoperazone.
Disulfiram-like effect
* Against Pseudomonas:
3°G Cef taz idime (taz taz taz taz)
4°G Cefepime, Cefpirome (not available in the USA)
Antipseudomonal penicillins
Aminoglycosides (synergy with beta-lactams)
Aztreonam (pseudomonal sepsis)
* Covers MRSA: Ceftaroline (rhymes w/ Caroline, Caroline the 5°G Ceph), Vancomycin, Daptomycin, Linezolid, Tigecycline.
* Covers VRSA: Linezolid, Dalfopristin/Quinupristin
* Aminoglycosides: decrease release of ACh in synapse and act as a Neuromuscular blocker, this is why it enhances effects of muscle relaxants.
* DEMECLOCYCLINE: tetracycline that’s not used as an AB, it is used as tx of SIADH to cause Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (inhibits the V2 receptor in collecting ducts)
* Phototoxicity: Q ue S T ion?
Q uinolones
Sulfonamides
T etracyclines

* p450 inhibitors: Cloramphenicol, Macrolides (except Azithromycin), Sulfonamides
* Macrolides SE: Motilin stimulation, QT prolongation, reversible deafness, eosinophilia, cholestatic hepatitis
* Bactericidal: beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, carbapenems), aminoglycosides, fluorquinolones, metronidazole.
* Baceriostatic: tetracyclins, streptogramins, chloramphenicol, lincosamides, oxazolidonones, macrolides, sulfonamides, DHFR inhibitors.
* Pseudomembranous colitis: Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Clindamycin, Lincomycin.
* QT prolongation: macrolides, sometimes fluoroquinolones
-
 neuronium reblogged this · 2 years ago
neuronium reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 lepau123 reblogged this · 5 years ago
lepau123 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 explorer1270 liked this · 6 years ago
explorer1270 liked this · 6 years ago -
 estippete-blog liked this · 6 years ago
estippete-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 justanotherdna reblogged this · 6 years ago
justanotherdna reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 a-memoir-of-a-sad-life liked this · 6 years ago
a-memoir-of-a-sad-life liked this · 6 years ago -
 scientistunderconstruction-blog liked this · 6 years ago
scientistunderconstruction-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 beanlop liked this · 7 years ago
beanlop liked this · 7 years ago -
 magnificentpersondonutwomba-blog liked this · 7 years ago
magnificentpersondonutwomba-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 flaviusanghel27-blog liked this · 7 years ago
flaviusanghel27-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 justanotherdna reblogged this · 7 years ago
justanotherdna reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 justanotherdna liked this · 7 years ago
justanotherdna liked this · 7 years ago -
 ananadiah89 liked this · 7 years ago
ananadiah89 liked this · 7 years ago -
 purplebee13 liked this · 7 years ago
purplebee13 liked this · 7 years ago -
 myopticvision123 liked this · 7 years ago
myopticvision123 liked this · 7 years ago -
 madameliliana1001 liked this · 7 years ago
madameliliana1001 liked this · 7 years ago -
 retropearls liked this · 8 years ago
retropearls liked this · 8 years ago -
 chickendoodlesmerpderp liked this · 8 years ago
chickendoodlesmerpderp liked this · 8 years ago -
 jodran2005 liked this · 8 years ago
jodran2005 liked this · 8 years ago -
 virologistandpotato reblogged this · 8 years ago
virologistandpotato reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 crazyseasons reblogged this · 8 years ago
crazyseasons reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 crazyseasons liked this · 8 years ago
crazyseasons liked this · 8 years ago -
 full-of-seoul liked this · 8 years ago
full-of-seoul liked this · 8 years ago -
 thecupofstanley liked this · 8 years ago
thecupofstanley liked this · 8 years ago -
 knowledgemd reblogged this · 8 years ago
knowledgemd reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 knowledgemd liked this · 8 years ago
knowledgemd liked this · 8 years ago -
 knowledgemd reblogged this · 8 years ago
knowledgemd reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 nelkitty reblogged this · 8 years ago
nelkitty reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 crazy939-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
crazy939-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 crazy939-blog liked this · 8 years ago
crazy939-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 agent--pizza reblogged this · 8 years ago
agent--pizza reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 thewildkidinside liked this · 8 years ago
thewildkidinside liked this · 8 years ago -
 shamelesszombiealpaca reblogged this · 8 years ago
shamelesszombiealpaca reblogged this · 8 years ago