Neptune And Its Moons (Proteus, Larissa, Despina And Galatea)

Neptune and its moons (Proteus, Larissa, Despina and Galatea)
Credit: NASA / Hubble (infrared)
More Posts from Sidusglacies and Others

What drives auroras on Saturn? To help find out, scientists have sorted through hundreds of infrared images of Saturn taken by the Cassini spacecraft for other purposes, trying to find enough aurora images to correlate changes and make movies. Once made, some movies clearly show that Saturnian auroras can change not only with the angle of the Sun, but also as the planet rotates. Furthermore, some auroral changes appear related to waves in Saturn's magnetosphere likely caused by Saturn's moons. Pictured here, a false-colored image taken in 2007 shows Saturn in three bands of infrared light. The rings reflect relatively blue sunlight, while the planet itself glows in comparatively low energy red. A band of southern aurora in visible in green. In has recently been found that auroras heat Saturn's upper atmosphere. Understanding Saturn's auroras is a path toward a better understanding of Earth's auroras.
Image Credit: NASA, Cassini, VIMS Team, U. Arizona, U. Leicester, JPL, ASI
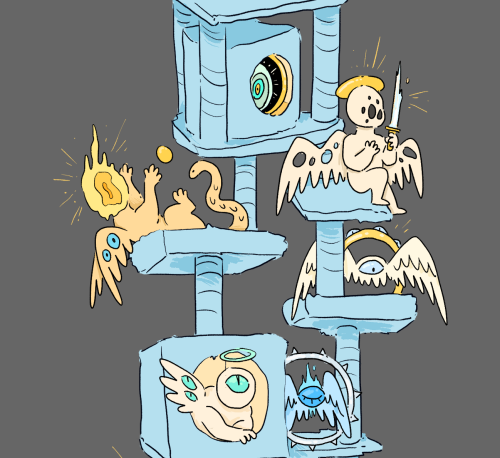


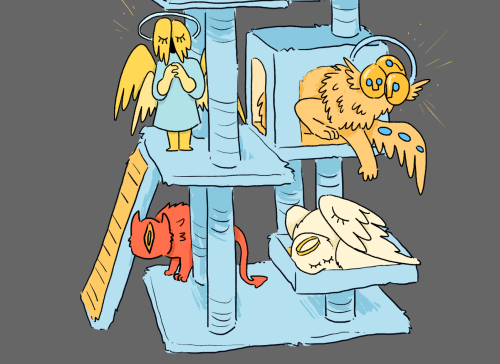
I had to build some cat furniture and it made me think of a heavenly cat tree.
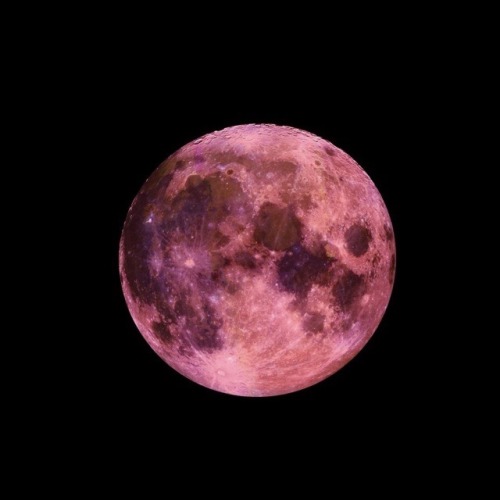
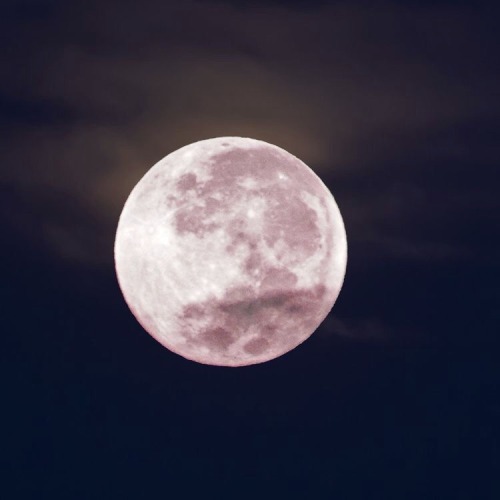
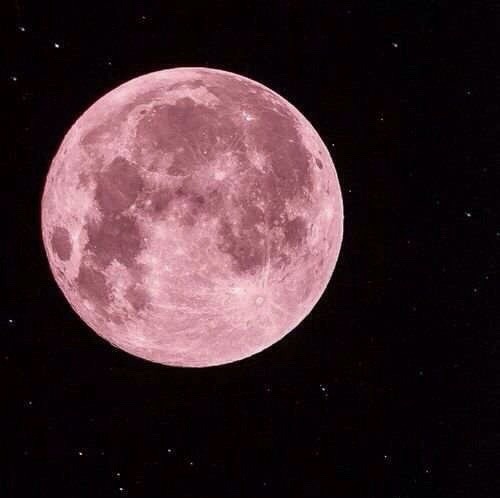
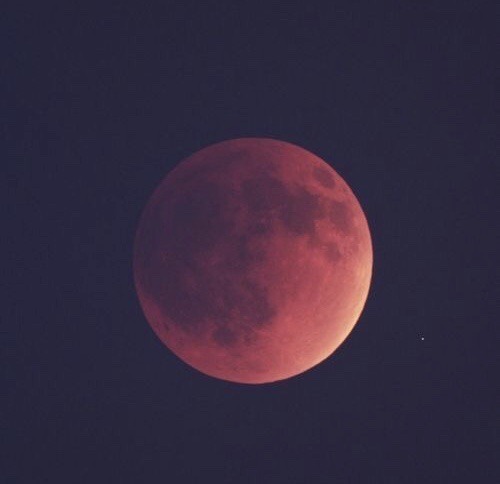
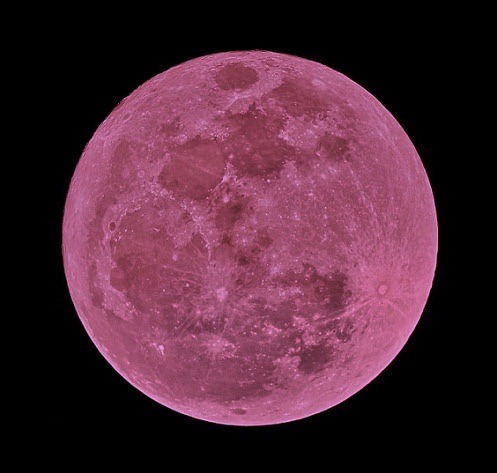
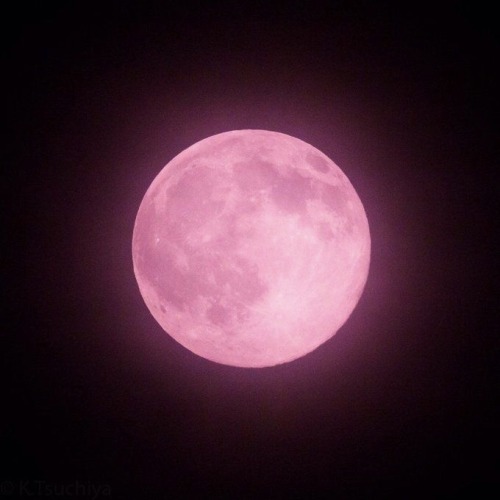









the moon is a loyal companion
Light pillars are a rare optical phenomenon in which ice crystals in the atmosphere reflect sources of light in a vertical formation. Long, illuminated beams can form above or below sources of artificial or natural light due to the air being extremely cold.




Charon, moon of Pluto, observed by NASA's New Horizons probe just before closest approach on this day in 2015. (It flew within 12,500 km of Pluto and as close as 27,000 km to Charon.)
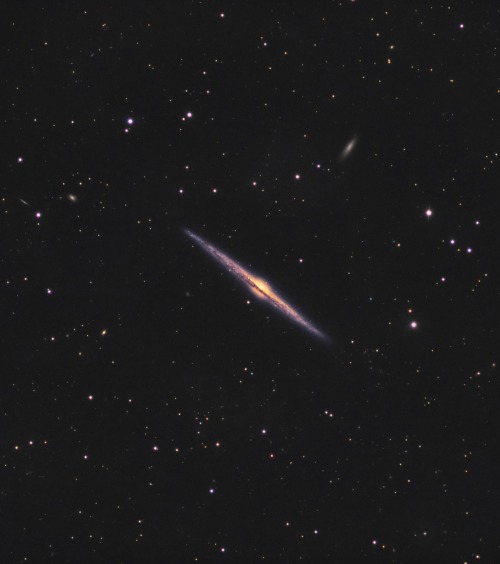




The needle galaxy is nearly 50 million light-years away. Reddit user chucksastro used 11 hours of exposure time to capture this image from his backyard.



Undulatus asperatus
Undulatus asperatus is a new separate cloud classification currently on petition to be added to the official list of observable cloud types. If accepted as a distinct cloud type, it will be the first addition to the list of cloud types since cirrus intortus was added in 1951. It was proposed by the founder of The Cloud Appreciation Society. Recognition of the cloud classification is still pending.
The experience of these clouds is as if, it is said, one were below the Sea looking up at the surface of the water. Yet when they occur, there reportedly is little to no turbulence at the land surface. The clouds are most common in the Great Plains of the United States following thunderstorm activity in the earlier parts of the day.

Like Earth, Jupiter is home to polar auroras that light the sky as charged particles interact with the planet’s magnetosphere. A recent paper identifies interesting features in the aurora that appear similar to expanding vortex rings.(Image credit: Jupiter - NASA, ESA, and J. Nichols, aurora features - NASA/SWRI/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/V. Hue/G. R. Gladstone/B. Bonfond; research credit: V. Hue et al.; via Gizmodo)
-
 leextacy liked this · 1 month ago
leextacy liked this · 1 month ago -
 love-n-purple liked this · 1 month ago
love-n-purple liked this · 1 month ago -
 downtothemarrow liked this · 1 month ago
downtothemarrow liked this · 1 month ago -
 samojakoiuglavu liked this · 1 month ago
samojakoiuglavu liked this · 1 month ago -
 flowyello liked this · 1 month ago
flowyello liked this · 1 month ago -
 petrovouho reblogged this · 1 month ago
petrovouho reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 petrovouho liked this · 1 month ago
petrovouho liked this · 1 month ago -
 nismo-na-filmu-zaboga reblogged this · 1 month ago
nismo-na-filmu-zaboga reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 nismo-na-filmu-zaboga liked this · 1 month ago
nismo-na-filmu-zaboga liked this · 1 month ago -
 if-we-die-we-die-cool reblogged this · 1 month ago
if-we-die-we-die-cool reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 if-we-die-we-die-cool liked this · 1 month ago
if-we-die-we-die-cool liked this · 1 month ago -
 lilachoneymoons reblogged this · 1 month ago
lilachoneymoons reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 imageness-retro reblogged this · 1 month ago
imageness-retro reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 imageness-retro liked this · 1 month ago
imageness-retro liked this · 1 month ago -
 h-jk-k reblogged this · 1 month ago
h-jk-k reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 thedowntown500 reblogged this · 1 month ago
thedowntown500 reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 leextacy reblogged this · 1 month ago
leextacy reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 writer-unblocked reblogged this · 1 month ago
writer-unblocked reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 pararrayos reblogged this · 1 month ago
pararrayos reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 pararrayos liked this · 1 month ago
pararrayos liked this · 1 month ago -
 simply-sithel liked this · 1 month ago
simply-sithel liked this · 1 month ago -
 hunter-gatherer-stuff reblogged this · 1 month ago
hunter-gatherer-stuff reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 sunbeamsandmoonrays liked this · 1 month ago
sunbeamsandmoonrays liked this · 1 month ago -
 g33kmama liked this · 1 month ago
g33kmama liked this · 1 month ago -
 lurker-no-more reblogged this · 1 month ago
lurker-no-more reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 cat-in-a-fedora liked this · 1 month ago
cat-in-a-fedora liked this · 1 month ago -
 shapeshifting-entity liked this · 2 months ago
shapeshifting-entity liked this · 2 months ago -
 sunbeacon reblogged this · 2 months ago
sunbeacon reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 annakin14 reblogged this · 2 months ago
annakin14 reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 annakin14 liked this · 2 months ago
annakin14 liked this · 2 months ago -
 whipsybask reblogged this · 2 months ago
whipsybask reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 lurker-no-more liked this · 2 months ago
lurker-no-more liked this · 2 months ago -
 gorgona-chingona liked this · 2 months ago
gorgona-chingona liked this · 2 months ago -
 floggingink reblogged this · 2 months ago
floggingink reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 sansakarstark reblogged this · 2 months ago
sansakarstark reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 malvarmenta reblogged this · 2 months ago
malvarmenta reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 lakeshirtsecurity liked this · 2 months ago
lakeshirtsecurity liked this · 2 months ago -
 mukeclemmings16 liked this · 2 months ago
mukeclemmings16 liked this · 2 months ago -
 lobinhasolitaria reblogged this · 2 months ago
lobinhasolitaria reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 catlizard liked this · 2 months ago
catlizard liked this · 2 months ago -
 catlizard reblogged this · 2 months ago
catlizard reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 captainquixotic liked this · 2 months ago
captainquixotic liked this · 2 months ago -
 lovecore liked this · 2 months ago
lovecore liked this · 2 months ago -
 cristinaricci reblogged this · 2 months ago
cristinaricci reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 planet-sb0 reblogged this · 2 months ago
planet-sb0 reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 2oowicky liked this · 2 months ago
2oowicky liked this · 2 months ago -
 caaasaaa liked this · 2 months ago
caaasaaa liked this · 2 months ago -
 gods-bath-room-floor reblogged this · 2 months ago
gods-bath-room-floor reblogged this · 2 months ago
